Choose your operating system:
Windows
macOS
Linux
A Sprite in Paper 2D is a Texture Mapped Planar Mesh and associated Material that can be rendered in the world, created entirely within Unreal Engine 4 (UE4). In simpler terms, it's a quick and easy way to draw 2D images in UE4.
Sprites can also be edited inside UE4 in the Sprite Editor which offers four modes: View for previewing the sprite and general statistics, Edit Source Region which displays the full source texture and allows you to set the area within the source texture that composes the individual sprite, Edit Collision displays and allows editing of the sprite collision shapes, and Edit RenderGeom which displays and allows editing of the sprite render geometry.
Once you have a collection of Sprite assets, you can then begin animating them by creating a Flipbook which sequentially will play through the Sprites added to the Flipbook. See the Flipbook documentation for more information.
Creating Sprites
Sprites are created in the Content Browser , like other assets. They can be created from scratch as blank assets, generated from other existing assets, or created using imported data.
Blank Sprite Asset
To create a new blank Sprite asset:
-
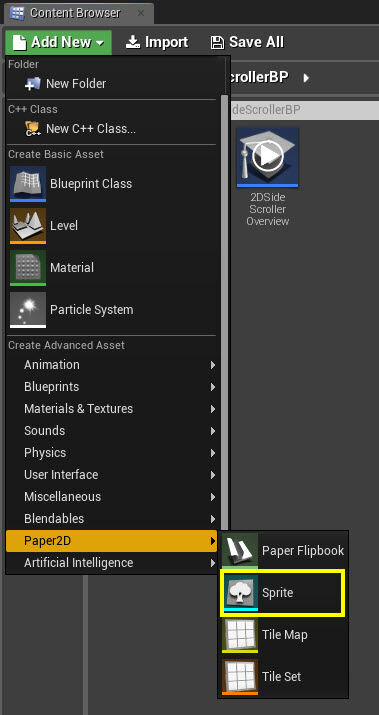
Click the Add New button in the Content Browser , then under Paper2D , select Sprite .
![SpriteCB.jpg]()
You can also Right-click in the Content Browser to bring up the same context menu.
-
Name the new Sprite asset.
![MySpriteCB.jpg]()
-
The Sprite has been created but has not been saved yet (indicated by the asterisk in the lower-left corner).
![SpriteSaveAll.jpg]()
Click the Save All button to save the Sprite.
-
Double-click the new Sprite asset to open it in the Sprite Editor .
-
In the Details panel, you can assign a Texture to the Sprite asset using the Source Texture property.
![DetailsSprite.jpg]()
See the Sprite Editor Reference documentation for information on working with Sprites in the Sprite Editor .
Single Sprite from Texture
To create a sprite from an existing Texture asset:
-
In the Content Browser , Right-click on the Texture asset, then under Sprite Actions choose Create Sprite .
![ChooseSprite.jpg]()
-
Name the new Sprite asset.
![sprite_create_name.png]()
Series of Sprites from Sprite Sheet Texture
To create a series of Sprites from a Sprite Sheet Texture:
-
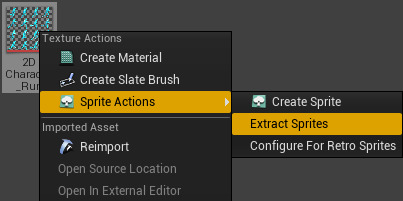
In the Content Browser , Right-click on the Sprite Sheet Texture, then under Sprite Actions choose Extract Sprites .
![sprite_extract_menu.png]()
-
Individual Sprites will be automatically extracted and added to the Content Browser .
![sprite_extract_result.png]()
Importing from a JSON file
Paper 2D includes an importer for JSON formatted sprite sheet descriptions, which can be exported from tools like Adobe Flash CS6 or Texture Packer . It will import any referenced textures and create sprite assets for each sprite. The importer also assumes that all of the sprites are frames of an animation, so it will always create a Flipbook in addition to the individual sprites. You can delete the generated flipbook if it is not needed.
See Paper 2D Import Options for more information on Importing Options.
Creating Sprite Materials
The Paper 2D plugin includes a set of basic Materials that sample a Texture and multiply it by the Vertex Color, with Lit and Unlit variations for Opaque, Masked, and Translucent textures. The default Material on Sprites and Flipbooks is Unlit Masked.
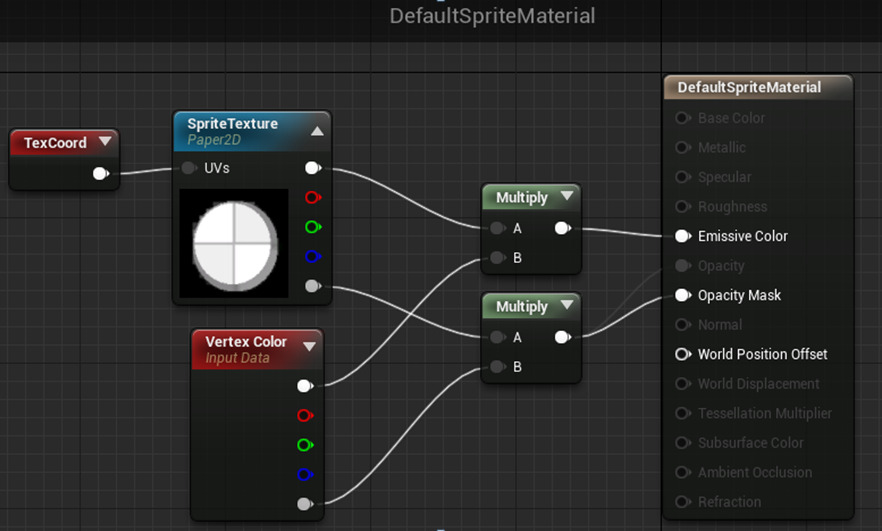
Creating Custom Sprite Materials
A custom Sprite Material can be created by duplicating one of the existing ones, or creating a new Material in the Content Browser . When a Sprite is rendered, the texture defined in a Sprite asset will be piped into any texture parameters named SpriteTexture in the material. The SpriteTextureSampler node in the Material Editor can be placed to do this automatically. Sprite instances will pass in their color as a Vertex Color, but it can be used for anything in the material, not just tinting.