Choose your operating system:
Windows
macOS
Linux
This page will cover the various properties of the Pivot Painter 2 3DS Max script. This tool is used to create very complex animations by storing pivot and rotational information about the model inside of its textures. This MAXScript can be used create complex hierarchies of animations all driven by Material's inside of Unreal Engine 4.

Prep Tools
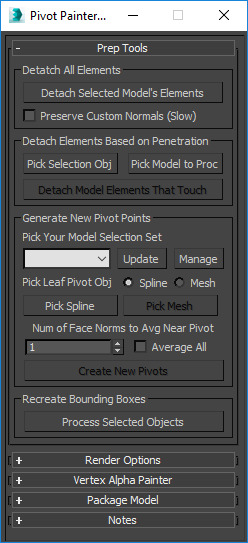
|
Property |
Description |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Detach Selected Model's Elements |
This will detach every element in an object as its own object. |
||||||
|
Preserve Custom Normals (Slow) |
This will duplicate the model as many times as there are model elements and then delete all but one element from each copy. This is to preserve the meshes custom normals. This method can potentially be very time-consuming depending on the number of elements being detached since the model will be duplicated for each element there is. It is recommended to only use this is absolutely necessary. |
||||||
|
Detach Elements Based on Penetration |
|||||||
|
Pick Selected Obj |
Pick an editable polygon object without any modifiers applied. Do not pick the same object for both the "selection object" and the "model to process" options. (Note: The selection mesh cannot have any holes.) |
||||||
|
Pick Model to Proc |
Pick an editable polygon object without any modifiers applied. Do not pick the same object for both the "selection object" and the "model to process" options. (Note: The selection mesh cannot have any holes.) |
||||||
|
Detach Model Elements That Touch |
This will separate any elements that touch or penetrate the selection object's geometry into its own separate object. (Note: This tool will not work properly if the selection object has any holes.) |
||||||
|
Generate New Pivot Points |
|||||||
|
Pick Your Model Selection Set |
Use this drop-down to select your model selection set.
|
||||||
|
Pick Leaf Pivot Obj |
Choose whether you would like to construct your pivots based off of the knots in a spline or the vertices in an editable poly object. This will enable the button selections for Pick Spline or Pick Mesh
|
||||||
|
Num of Face Norms to Avg Near Pivot |
Enter a value to specify the number of face normals you want to average near a pivot point. This enables you to control the number of normals you're affecting or you can simply enable the Average All checkbox to include all available face normals nearest the pivot. |
||||||
|
Create New Pivots |
This will generate a new pivot point for every editable polygon object in the selection set. The pivot will rest on the model vertex closest to a knot in the selected spline or vertex in the chosen editable poly object. The x-axes of the pivots will be oriented toward the averaged center of the meshes. The meshes' bounds will also be recreated and aligned with the new pivot. |
||||||
|
Recreate Bounding Boxes |
|||||||
|
Process Selected Objects |
As a model changes from via sub-object manipulation, its bounding box expands to fix the model elements but does not re-align itself with the model's pivot point. This function recreates the object's bounding box so that it aligns with the model's basis vectors. It is necessary to have a correctly constructed bounding box to successfully utilize the axis tools in the processing section along with the vertex alpha painting tools. |
||||||
|
Property |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Update |
Press this to get the latest selection sets from 3DS Max. |
|
Manage |
Press this to manage your selection sets. |
|
Property |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Pick Spline |
Use this button to pick a spline from the scene viewport. The script will find the closest vertex pair between each model and each knot in the spline. Then it will move the object's pivot to the location of that vertex and orient the axis to match the model. The x-axis will point toward the center of the model from the desired vertex. The z-axis will point along the surface's normal. Processing time will increase as vertex counts rise. (Warning: Do not use the H list hotkey. The object must be picked from the viewport.) (Tip: For grass use a single or two-knot spline placed well below your grass to increase calculation speeds.) |
|
Pick Mesh |
Use this button to pick a mesh from the scene viewport. The script will find the closest vertex match between the model's pivot and model's vertices. Then it will orient the leaf's axis to the polygonal orientation and vertex position. Warning: Do not use the H list hotkey. The object must be picked from the viewport.) (Tip: For grass use a single or two-knot spline placed well below your grass to increase calculation speeds.) |
Render Options
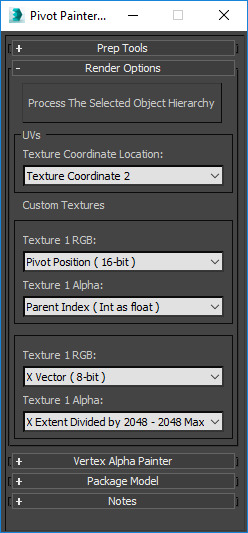
|
Property |
Description |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Process The Selected Object Hierarchy |
Select your mesh and then press paint. This script will locate all the editable polygon meshes that are connected to the selected mesh via their shared hierarchy. (One can connect one object to another via the 3DS Max Link tool.) After locating the meshes the script will then alter the UV channel you've chosen to act as the basis for the ensuing textures which will be generated. The default texture contains model information like pivot location in the images RGB channels and an index in the alpha. The index can be used to locate the current meshes parent mesh. This is made simple Pivot Painter 2.0 Material Functions in Unreal Engine 4. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
UVs |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Texture Coordinate Location |
Paint |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Custom Textures |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Texture 1 RGB |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Texture 1 Alpha |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Texture 2 RGB |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Texture 2 Alpha |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Vertex Alpha Painter
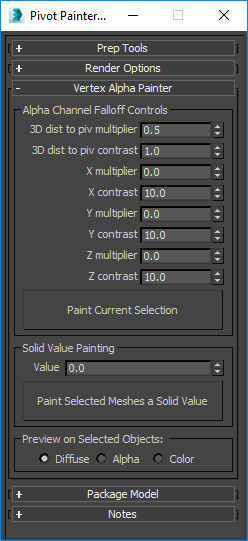
|
Property |
Description |
|
|---|---|---|
|
Alpha Channel Falloff Controls |
||
|
3D dist to piv multiplier |
This multiplies a distance calculation from the pivot to the current vertex. |
|
|
3D dist to piv contrast |
The contrast option is used as the exponent of a power function applied to a distance based on a gradient between the object's pivot point and the current vertex position. |
|
|
XYZ Multiplier |
Selectively increase and decrease the influence of local space gradients on X, Y, and Z. The gradient is formed by finding the distance between vertices and the object's center line, as defined by the object's pivot point and an axis direction. |
|
|
XYZ Contrast |
The exponent of a power function applied to the XYZ gradient results. |
|
|
Paint Current Selection |
This paints the editable polygon objects in the selection set using the parameters above. The objects that aren't collapsed editable polygon objects will be ignored. |
|
|
Solid Value Painting |
||
|
Value |
Use any value between 0 to 1 to be used to paint the selected meshes a solid color. A value of 0 will be black with 1 being full white. |
|
|
Paint Selected Meshes a Solid Value |
Fill the vertex alpha with a value of zero. This value can be referenced in an Unreal shader to isolate or remove animation from certain elements. |
|
|
Preview on Selected Objects |
||
|
Diffuse |
Click on the active viewport to view this new channel. |
|
|
Alpha |
Click on the active viewport to view this new channel. |
|
|
Color |
Click on the active viewport to view this new channel. |
|
Package Model
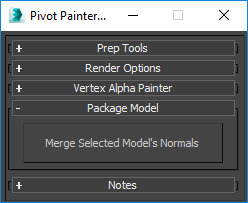
|
Property |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Merge Selected Model's Normals |
Select several models that contain touching, open edges. This feature will average out their normals to form a continuous surface. |