Choose your operating system:
Windows
macOS
Linux
The Image Adjustment functions exist as a way to perform basic color correction operations on textures. They are useful in that they allow corrective actions or variations on a texture without having to worry about the overhead of loading a separate version into memory.
Image Adjustment Functions
The following is a list of the functions found under the Image Adjustment category.
3ColorBlend
The 3ColorBlend function blends between 3 input colors based on a grayscale alpha, in the following manner:
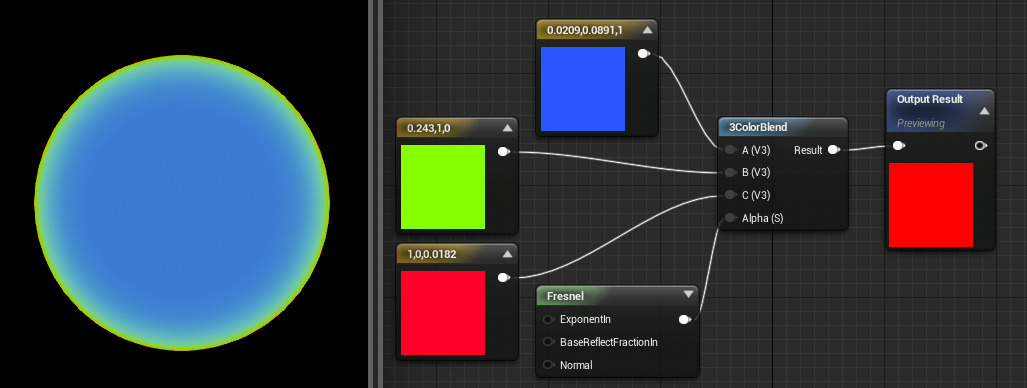
|
Alpha Tone |
Color |
|---|---|
|
Dark Tones |
Color A |
|
Midtones |
Color B |
|
Highlights |
Color C |
|
Item |
Description |
|
|---|---|---|
|
Inputs |
||
|
Color A (3Vector) |
This color will be applied wherever the alpha supplies dark tones to blacks. |
|
|
Color B (3Vector) |
This color will be applied wherever the alpha supplies midtones. |
|
|
Color C (3Vector) |
This color will be applied wherever the alpha supplies highlights to whites. |
|
|
Alpha (Scalar) |
This maps out where each color will be applied, as per above. |
|
CheapContrast
The CheapContrast function boosts the contrast of an input by remapping the high end of the histogram to a lower value, and the low end of the histogram to a higher one. This is similar to applying a Levels adjustment in Photoshop, and pulling the black and white flags in a bit. The user may control the degree to which the contrast is boosted.
|
Item |
Description |
|
|---|---|---|
|
Inputs |
||
|
In (Scalar) |
The channel or black and white image having its contrast boosted. |
|
|
Contrast (Scalar) |
How much to boost contrast. 0 is default, or no change. |
|
This function takes in a scalar value rather than RGB, meaning it is particularly suited to black and white images or single channels. For contrast boost on full-color images, use CheapContrast_RGB .

CheapContrast_RGB
The CheapConstrast_RGB function boosts the contrast of an input by remapping the high end of the histogram to a lower value, and the low end of the histogram to a higher one. This is similar to applying a Levels adjustment in Photoshop, and pulling the black and white flags in a bit. The user may control the degree to which the contrast is boosted.
Unlike the regular CheapContrast function , this function can take in a Vector3 as the input, allowing it to perform contrast operations on a color image.
|
Item |
Description |
|
|---|---|---|
|
Inputs |
||
|
In (Scalar) |
The base image having its contrast boosted. |
|
|
Contrast (Scalar) |
How much to boost contrast. 0 is default, or no change. |
|

SCurve
The SCurve function boosts contrast of an image by interpolating the values of each channel values of an image along an S-curve. This is similar to applying a Curves adjustment in Photoshop and setting the RGB curve to an S-curve or using the Increase Contrast (RGB) preset.
|
Item |
Description |
|
|---|---|---|
|
Inputs |
||
|
In (Scalar) |
The base image having its contrast boosted. |
|
|
Power (Scalar) |
How much to boost contrast. 1 is default, or no change. |
|

3PointLevels
The 3PointLevels function takes in an image and remaps the values of each channel across 3 points (white, black, middle). This is similar to applying a Levels adjustment in Photoshop. However, unlike the CheapContrast functions, this function provides full control in that it gives the user ability to adjust interpolation of lights, darks, and grays (gamma). By default, the three remapping points are interpolated linearly. However, you may input your own custom interpolation curve if you wish.
|
Item |
Description |
|
|---|---|---|
|
Inputs |
||
|
Texture (Scalar ) |
The input texture. |
|
|
New Black Value (Scalar) |
Set the new value for the previous value of 0. |
|
|
New Middle Value (Scalar) |
Replaces the old value that matches the Middle Point input value. |
|
|
New White Value (Scalar) |
Set the new value for the previous value of 1. |
|
|
Middle Point (Scalar) |
Pick a value from the input image that will get replaced with the value from Middle Point. |
|
|
Define Interpolation Curve (StaticBool) |
Set to true if you want to define your own interpolation curve using the Interpolation Power input. |
|
|
Interpolation Power (Scalar) |
A power node applied to the interpolation. This controls the interpolation between the three points (black, white, and middle). |
|
|
Invert Interpolation Power |
Set to true if you want to invert the power curve (this generally lowers contrast instead of boosting it). |
|

The "-------------" inputs of this node are merely separators in the list of inputs for sake of clarity. They are not intended to receive actual connections.
Like the CheapContrast function, this node takes in a scalar by default, meaning it is suited for single channels or black and white images.
HueShift
The HueShift function offsets the current hue value of an input color by a given percentage. This percentage is 1-based and centered around the color wheel. For instance, a shift of 0.5 (50%) will shift to a complimentary hue, or the hue on the opposite side of the color wheel. A shift of 1.0 (100%) gives no change, as this is the equivalent of rotating completely around the color wheel.
|
Item |
Description |
|
|---|---|---|
|
Inputs |
||
|
Hue Shift Percentage (Scalar) |
How far around the color wheel to shift the incoming hue. |
|
|
Texture (Vector3) |
The incoming texture having its hue shifted. |
|

SmoothThreshold
The SmoothThreshold function takes in a gradient, an interpolation rate, and a threshold value (Cutoff Value). It then applies a smooth contrast to the gradient, based on the inputs. Here is a breakdown of what each input does:
|
Item |
Description |
|
|---|---|---|
|
Inputs |
||
|
Cutoff Value |
Gradient input values that fall below the cutoff value will be affected by the operation. |
|
|
Lerp Value |
Add a negative or positive number to smoothly ramp to from the original values. Ramping occurs in values lower than the cutoff value. |
|
|
Gradient |
This value serves as the base for the contrast operation. |
|