Choose your operating system:
Windows
macOS
Linux
Unreal Engine 4 streamlines the process by which you can produce or modify ambient sounds through the use of the Ambient Sound Actor . When a Sound Wave or Sound Cue asset is placed in a level, an Ambient Sound Actor with that sound asset is created. The Ambient Sound Actor has several properties which are covered on this page that will allow you to modify how players receive the sound.
For more information on importing files as Sound Waves or modifying files through Sound Cues , refer to their respective pages for additional documentation.
Ambient Sound Actor

The Ambient Sound Actor (icons pictured at left) can be used for many purposes such as ambient looping sounds as well as non-looping sounds. Generally, the Ambient Sound Actor conforms to the real world where the closer you are to a sound, the louder it will appear. By comparison, a sound that is normally loud, may appear soft if it is further away.
If the Ambient Sound Actor is set to Auto Activate , it will immediately begin to play once it is created (at the beginning of play or on spawn), even if the player is not in a position to hear it.
The sound asset the Ambient Sound Actor points to will only play once per trigger unless specified as Looping in the Sound Wave or defined as part of a Sound Cue asset.
You can add an Ambient Sound Actor to your level in several ways:
The first is by selecting the Ambient Sound Actor from the Place Actors panel in the All Classes tab and dragging and dropping it into your level as seen below.
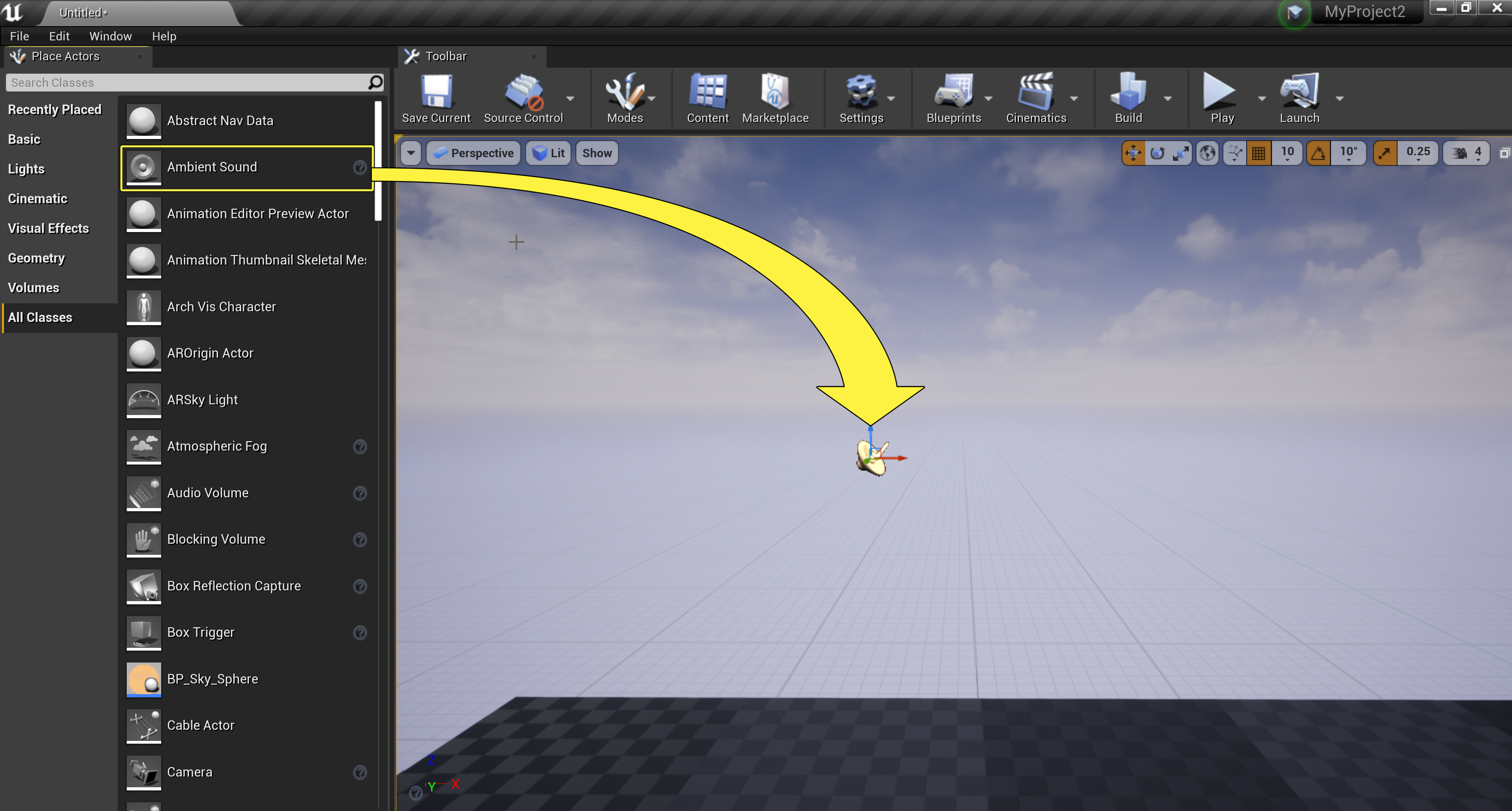
You can also highlight a Sound Wave or Sound Cue in the Content Browser and in your level, Right-click to bring up the context menu and select Place Actor .

Lastly, you can simply Left-click and drag a Sound Wave or Sound Cue from the Content Browser into your level.
Sound Properties
An Ambient Sound Actor has no function without an associated sound asset.
You can assign a sound asset from the
Details
panel by selecting an asset from the
Sound
setting's drop-down menu or by highlighting a sound asset in the
Content Browser
and clicking the


Once a Sound Cue asset has been assigned as the associated sound, the Edit option will become available so that you can open the Sound Cue asset up for editing inside the Sound Cue Editor . Optionally, instead of assigning a sound asset, you can select the New option which will create a new Sound Cue asset and will open it in the Sound Cue Editor for editing.
The Play and Stop options allow you to preview the assigned sound inside the editor and will play and stop playing the sound respectively.
Additional options inside the Sound section of the Details panel are defined below.
|
Property |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Sound |
Points to a Sound Wave or Sound Cue asset. |
|
Is UI Sound |
Whether or not the sound asset plays when the game is paused. |
|
Volume Multiplier |
Modifier applied to set the overall Volume of the sound. |
|
Pitch Multiplier |
Modifier applied to set the overall Pitch of the sound. |
|
Instance Parameters |
Allows adding of per-instance parameters for the sound. |
|
Sound Class Override |
Is an optional group that can be assigned for the sound asset. |
Attenuation Properties
Attenuation is the ability of a sound to decrease in volume as the player moves away from it. It works using two radii: MinRadius and MaxRadius. As you move from the sound's origin through the MinRadius, the volume of the sound is at 100%. As you move within the space between the MinRadius and the MaxRadius, the volume level is adjusted based on the Distance Algorithm . Outside of the MaxRadius, the volume of the sound is at 0%.
For additional information on Attenuation, please refer to the Sound Attenuation page.
The options under the Attenuation section that can be modified inside the Details panel are defined below:

|
Property |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Allow Spatialization |
Enables/Disables whether or not the audio component is spatialized. |
|
Override Attenuation |
Uses the asset's Attenuation settings or the Attenuation Override's settings. |
|
Attenuation Settings |
Points to and uses the settings assigned inside a SoundAttenuation asset. |
|
Attenuation Overrides |
Overrides and allows you to modify the Attenuation settings. |
It is advisable to use Sound Attenuation objects whenever possible, if for no other reason than to give broad control over the settings for many Actors.
When Override Attenuation is checked, the ability to set additional Attenuation settings becomes available:
|
Property |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Attenuate |
Enables the use of attenuation via volume. |
|
Spatialize |
Enable the source to be positioned in 3D. |
|
Distance Algorithm |
The type of volume versus distance algorithm to use for the attenuation model. |
|
Attenuation Shape |
The shape of the attenuation volume. |
|
Radius |
The overall size of the volume. By default, the volume shape is set to Sphere . This option will change based on the Attenuation Shape selected. |
|
Falloff Distance |
The distance over which falloff occurs. |
|
Non-Spatialized Radius |
At what distance to start treating the sound source as spatialized. |
|
Attenuate with LPF |
Enables attenuation via Low Pass Filter. |
|
LPFRadius Min |
The range at which to start applying a Low Pass Filter. |
|
LPFRadius Max |
The range at which to apply the maximum amount of Low Pass Filter. |
To allow for more control over the Attenuation volume, Unreal Engine 4 allows you to set the Attenuation Shape to four different volume types: Sphere, Capsule , Box , or Cone . In general, a Sphere volume is a reasonable choice, but there may be instances when you want finer control over the way the volume fits inside your levels. For example, filling a square room with a Box volume makes more sense.
Modulation Properties
The Modulation settings allow you to control the min/max modulation for both Pitch and Volume as well as set a High Frequency Gain Multiplier.

|
Property |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Pitch Modulation Min |
The lower bound to use when randomly determining a pitch multiplier. |
|
Pitch Modulation Max |
The upper bound to use when randomly determining a pitch multiplier. |
|
Volume Modulation Min |
The lower bound to use when randomly determining a volume multiplier. |
|
Volume Modulation Max |
The upper bound to use when randomly determining a volume multiplier. |
|
High Frequency Gain Multiplier |
A multiplier to apply to the high frequency gain for sounds generated by this component. |
Adding Audio Components To Blueprints
Inside a Blueprint , in the Component panel, select the Add Component button and select the Audio component.

The Audio component can be referenced through Blueprints and many of its settings can be altered by using different types of functions.
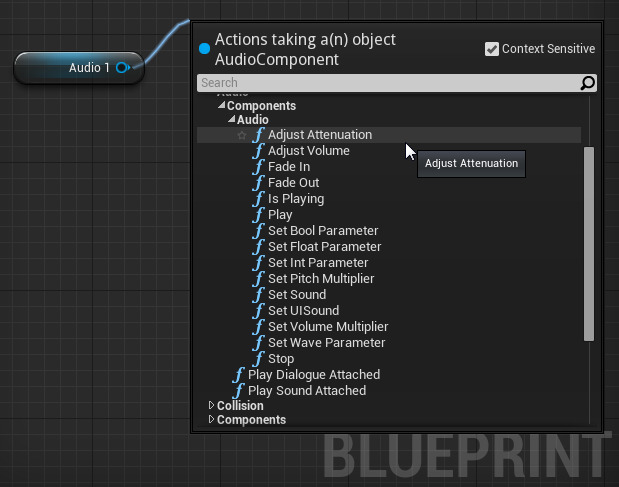
The Audio component does have a unique event which can be used. This OnAudioFinished event allows you to fire off events when the audio is finished playing or is stopped prematurely with a Stop function.
Audio Volumes
For an added level of control, you can include Audio Volumes in conjunction with Ambient Sound Actors . For more information on how to use an Audio Volume, refer to the Audio Volumes section of the Volumes page.
Making changes to an Audio Volume will not work in realtime inside the editor. You will need to rebuild the geometry of the level that contains the edited volume in order for your changes to take effect.