The Spring Arm component is used to automatically control how the camera handles situations where it becomes obstructed.
Choose your operating system:
Windows
macOS
Linux
Choose your implementation method:
C++
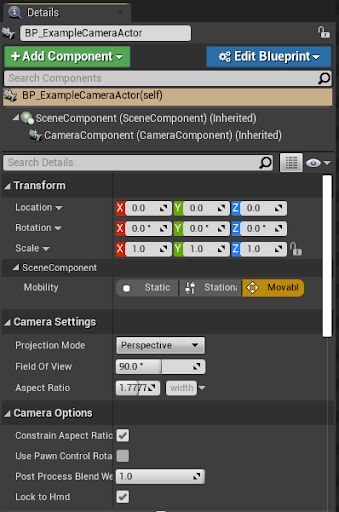
The following table is an overview of each section in the Details panel for a Camera Actor.
|
Property |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Transform |
This category represents the location of the Camera in the world. |
|
Camera Settings |
This category allows you to modify the type of projection used by the Camera, field of view, aspect ratio, and post process blending. |
|
Auto Player Activation |
Specifies which Player Controller, if any, should automatically use this Camera when the controller is active. |
|
Film |
In this category, you can apply film effects such as Tint, Saturation, or Contrast. See also Film . |
|
Scene Color |
Used to apply effects to the Camera. See also Scene Color . |
|
Bloom |
Simulates the effects the eye perceives when viewing bright objects. See also Bloom . |
|
Light Propagation Volume |
Used to achieve Global Illumination (GI) in real-time. See also Light Propagation Volumes . |
|
Ambient Cubemap |
Lights the scene from a provided image. See also Ambient Cubemap . |
|
Auto Exposure |
This simulates the human eye adjusting to bright/dark areas. See also Auto Exposure . |
|
Lens Flares |
Simulates the scattering of light when viewing bright objects through imperfections found in camera lenses. See also Lens Flares . |
|
Ambient Occlusion |
Approximates the attenuation of light due to occlusion. See also Ambient Occlusion . |
|
Global Illumination |
Affects the indirect lighting contribution coming from Lightmass in order to alter a scene's brightness, color, or tint. See also Global Illumination . |
|
Depth Of Field |
Applies a blur effect to a scene based on distance in front or behind a focal point. See also Depth Of Field . |
|
Motion Blur |
Generates a Motion Blur effect that blurs objects based on its motion. See also Motion Blur . |
|
Misc |
Applies Blendables (screen overlays), sets Anti-Aliasing methods or Screen Percentage options for the Camera. See also Blendables , Screen Percentage , or AA Method . |
|
Screen Space Reflections |
Alters the appearance of objects on the surface of Materials. Enabled by default. See also Screen Space Reflection . |
|
Activation |
Determines whether or not the Camera is automatically enabled. |
|
Tags |
Allows you to place Tags on the Actor. |
|
Actor |
Displays information pertaining to the Camera Actor itself. |
|
Blueprint |
Allows you to turn the Actor into a Blueprint or add Events to the Level Blueprint for the Actor. |
For information on using Cameras for cinematic purposes, refer to Sequencer Overview overview page. Additionally, the Sequencer Subway provides an excellent resource for a sample cutscene and how it was constructed.
Now that you have an understanding of how to place a Camera Actor in your level, the examples below provide some ways in which you can use the Camera, including how to use a Camera as a viewpoint for a player, how to use a Camera Component as part of an Actor class, how to use a Spring Arm Component with a Camera Component (typically used for creating Third Person perspectives), and how to switch between Cameras during gameplay.
Implementation Guides
![]()
The Spring Arm component is used to automatically control how the camera handles situations where it becomes obstructed.
![]()
A how-to page on modifying existing scripting logic from the Using Static Cameras page to blend between multiple Camera Actors viewpoints in the level.
A how-to page on modifying existing scripting logic from the Using Static Cameras page to blend between multiple Camera Actors viewpoints in the level.
![]()
How to add a Camera Component to a Character class and use it as a camera for any Actor in a level.
How to add a Camera Component to a Character class and use it as a camera for any Actor in a level.
![]()
A how-to guide for using a static camera to blend between player viewpoints.
A how-to guide for using a static camera to blend between player viewpoints.