Choose your operating system:
Windows
macOS
Linux
AppendVector
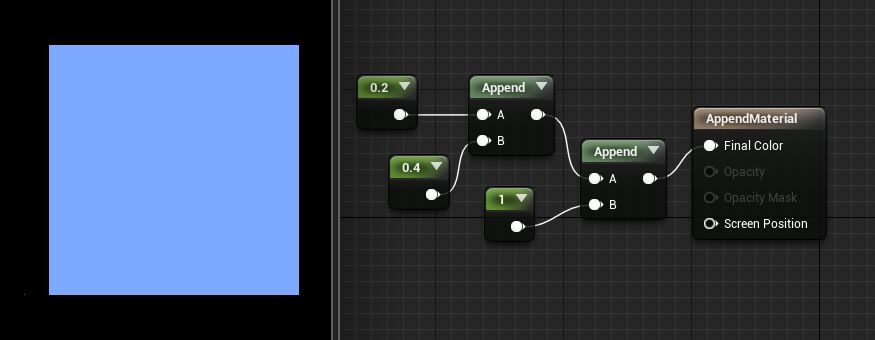
The AppendVector expression allows you to combine channels together to create a vector with more channels than the original. For example, you can take two individual Constants values and append them to make a two-channel Constant2Vector value. This can be useful for reordering the channels within a single texture or for combining multiple grayscale textures into one RGB color texture.
|
Item |
Description |
|
|---|---|---|
|
Inputs |
||
|
A |
Takes in the value(s) to append to. |
|
|
B |
Takes in the value(s) to be appended. |
|
Examples: Append of 0.2 and 0.4 is (0.2,0.4); Append of (0.2,0.4) and (1.0) is (0.2,0.4,1.0).
ComponentMask
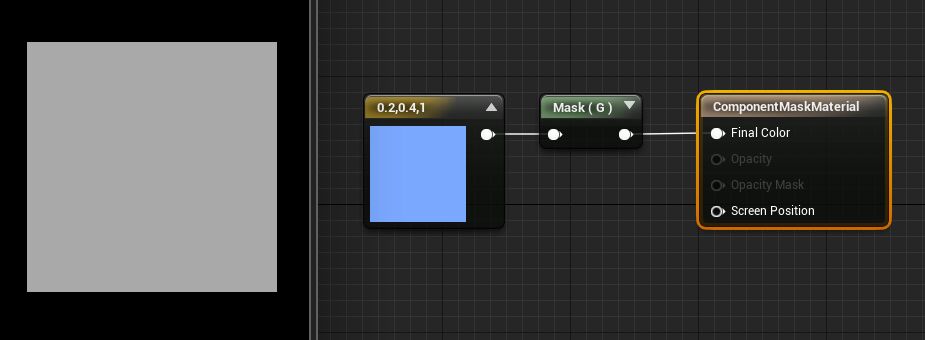
The ComponentMask expression allows you to select a specific subset of channels (R, G, B, and/or A) from the input to pass through to the output. Attempting to pass a channel through that does not exist in the input will cause an error, unless the input is a single constant value. In that case, the single value is passed through to each channel. The current channels selected to be passed through are displayed in the title bar of the expression.
|
Item |
Description |
|
|---|---|---|
|
Properties |
||
|
R |
If checked, the red (first) channel of the input value will be passed through to the output. |
|
|
G |
If checked, the green (second) channel of the input value will be passed through to the output. |
|
|
B |
If checked, the blue (third) channel of the input value will be passed through to the output. |
|
|
A |
If checked, the alpha (fourth) channel of the input value will be passed through to the output. |
|
Examples: ComponentMask with an input of (0.2,0.4,1.0) and the G channel will produce an output of (0.4), which appears as a 40% bright grayscale value when used as a color vector.
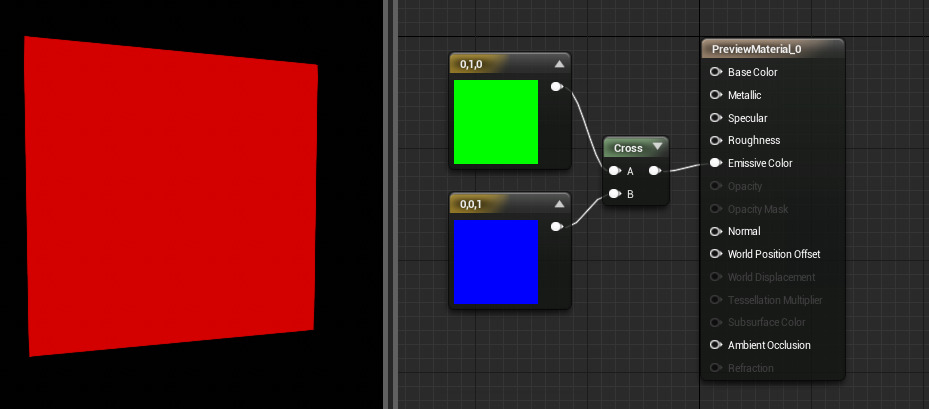
CrossProduct
The CrossProduct expression computes the cross product of two three-channel vector value inputs and outputs the resulting three-channel vector value. Given two vectors in space, the cross product is a vector that is perpendicular to both of the inputs.
|
Item |
Description |
|
|---|---|---|
|
Inputs |
||
|
A |
Takes in a three-channel vector value. |
|
|
B |
Takes in a three-channel vector value. |
|
Example Usage: CrossProduct is often used to compute directions which are perpendicular to two other directions.
DeriveNormalZ
The DeriveNormalZ expression derives the Z component of a tangent space normal given the X and Y components and outputs the resulting three-channel tangent space normal. Z is calculated as Z = sqrt(1 - (x * x + y * y));
|
Item |
Description |
|
|---|---|---|
|
Inputs |
||
|
InXY |
Takes in the X and Y components of the tangent space normal in the form of a two-channel vector value. |
|

DotProduct
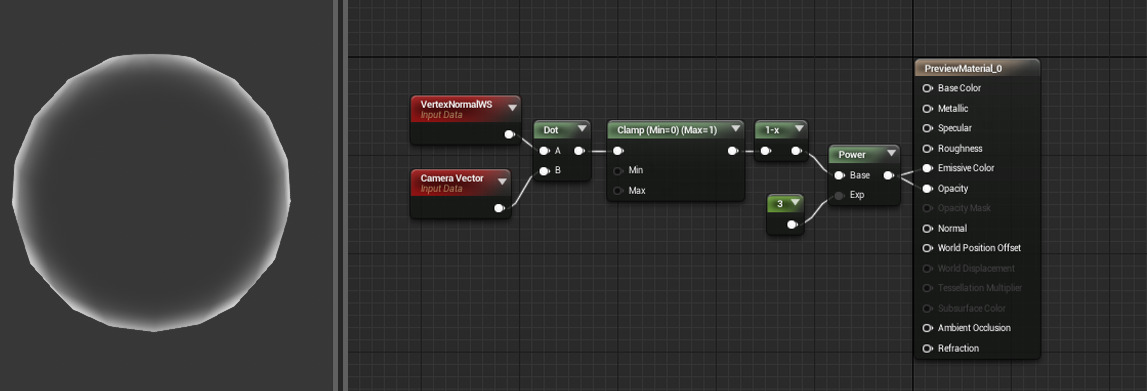
The DotProduct expression computes the dot product, which can be described as the length of one vector projected onto the other, or as the cosine between the two vectors multiplied by their magnitudes. This calculation is used by many techniques for computing falloff. DotProduct requires both vector inputs to have the same number of channels.
|
Item |
Description |
|
|---|---|---|
|
Inputs |
||
|
A |
Takes in a value or vector of any length. |
|
|
B |
Takes in a value or vector of the same length as A . |
|
Normalize
The Normalize expression calculates and outputs the normalized value of its input. Normalized vectors (also called "unit vectors") have an overall length of 1.0. This means each component of the input is divided by the total magnitude (length) of the vector.
Examples: Passing either (0,2,0) or (0,0.2,0) through Normalize will output (0,1,0). Passing (0,1,-1) through Normalize will output (0, 0.707, -0.707). The only special case is an all-zero vector, which will be unchanged.
It is not necessary to normalize an expression that plugs into the Normal material output.
Transform
The Transform expression converts a three-channel vector value from one reference coordinate system to another.
By default, all shader calculations in a material are done in tangent space. The vector constants, camera vector, light vector, etc are all transformed to tangent space before being used in a material. The Transform expression allows these vectors to be transformed from tangent space to world-space, local-space, or view-space coordinate systems. In addition, it allows world-space and local-space vectors to be transformed to any of the other reference coordinate systems.
|
Item |
Description |
|
|---|---|---|
|
Properties |
||
|
Source |
Specifies the current coordinate system to transform the vector from. This can be one of: World, Local, or Tangent. |
|
|
Destination |
Specifies the target coordinate system to transform the vector to. This can be one of: World, View, Local, or Tangent. |
|
The Transform node accounts for mirrored UVs, thus allowing, for example, highlights that only affect the right edge of a character.
The Transform node is useful for generating world space normals for sampling a cubemap. A normal map can be transformed to world space. Below is an example of transforming normals to world space in order to sample a cubemap:
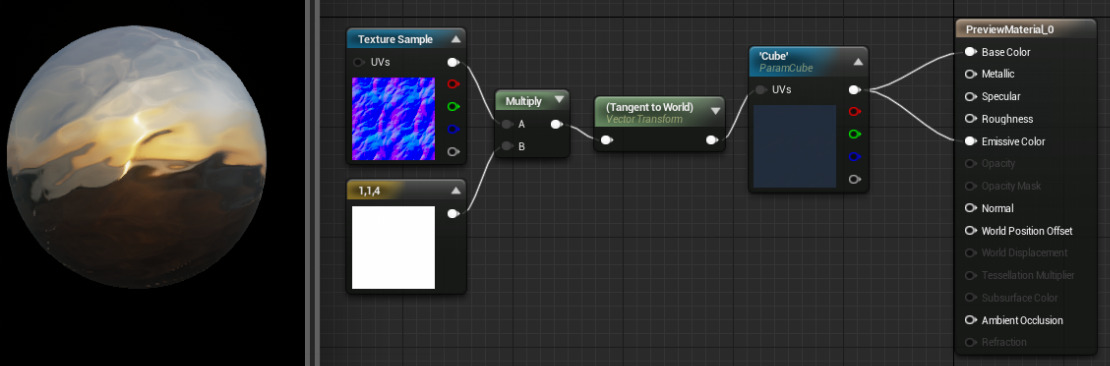
Transforming normals to view space can be used for creating edge-on effects. This can be achieved by using mesh normals to generate texture coordinates (commonly referred to as "Sphere Mapping"). With this method, normals facing directly at the camera will map to the center of the texture coordinates, and normals facing perpendicular to the camera will map at the edge of the texture coordinates. Here is an example of Sphere Mapping:

A constant3vector with a value of (0,0,1) is fed into the Transform with TRANSFORM_View set, which is then passed through a ComponentMask (Passing through only R and G). Since the Transform will output a range of values from -1 to 1, we must bias the values to put them into the 0-1 range. This is done by multiplying by 0.5, and then adding 0.5. Then simply plug that into the Coordinates of a texture. Any texture will work; I made one with three rings so that the effect is obvious.

To use this effect with a normal map, simply substitute the Constant3Vector with a normal map texture.
Here is an example of this spheremap material applied to a blob-like rock mesh:

VertexColor is mutually exclusive with the Transform node due to limited interpolators. If you use both a Transform node and VertexColor, then VertexColor will come out all white.
The transform node currently does not handle non-uniform scaling correctly.
TransformPosition
This node is deprecated due to major precision problems when used to derive world pos away from the origin! Use the WorldPosition node instead.
The TransformPosition expression can transform any position from screen space to the destination space specified by the expression's TransformType variable. Currently only transforming into world space is supported. This expression can be used to get world space coordinates in the material. To visualize world position, you can plug it straight into emissive: