Choose your operating system:
Windows
macOS
Linux
This page contains information about requirements, settings, and console commands for the Virtual Texturing system.
Streaming Virtual Texture Settings
The following settings and properties are used in setting up and working with Streaming Virtual Texturing .
Project Settings
When you have activated Enable virtual texture support in your project, you'll have access to the following settings in the Project Settings window, under the Editor and Rendering categories.

Rendering Settings
The available rendering settings are located under the Engine > Rendering > Virtual Textures category in the Project Settings window.
|
Properties |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Enable virtual texture support |
When enabled, Textures can be streamed using the Virtual Texture system. Changing this setting requires restarting the editor. |
|
Enable virtual texture lightmaps |
Lightmaps will be baked to Virtual Textures. This means lightmaps will have all the advantages (and disadvantages) of Streaming Virtual Textures . Compared to traditional lightmap textures atlas sheets, VT enables all lighting for a level to fit into a single texture, increasing batching efficiency. Lighting must be rebuilt for the project for this change to take effect. Changing this setting requires restarting the editor. |
|
Tile size |
The size in pixels for Virtual Texture Tiles. All values not a power of 2 will be rounded to the next power of 2 value. Changing this setting requires restarting the editor. |
|
Tile border size |
The size in pixels for Virtual Texture Tile Borders. All values not a power of 2 will be rounded to the next power of 2 value. Larger borders enable a higher degree of anisotropic filtering but uses more disk/cache memory. Changing this setting requires restarting the editor. |
|
Feedback resolution factor |
Lower factors will increase Virtual Texture Feedback Resolution, which increases CPU/GPU overhead. However, it may decrease streaming latency, especially if Materials use many Virtual Textures. |
|
Enable Zlib compression |
Enables use of Zlib to compress Virtual Textures. This makes VT textures smaller on disk I/O cost (number of reads or writes) but adds CPU cost to decompress. Changing this setting requires restarting the editor. |
|
Enable Crunch compression |
Enables use of Crunch library to compress Virtual Textures. Crunch is an open-source compression library designed to further compress GPU block-compressed textures (using DXT/BC/ETC compression). It makes data much smaller than Zlib, and decreases CPU cost to decompress. However, compression is lossy so the image quality will be reduced. When enabled, Crunch will only be used for supported texture formats. The degree of lossy compression applied can be controlled per-VT Asset by changing the Lossy Compression Amount property in the Texture Editor. The default value will apply minimal compression, resulting in the highest quality and largest memory usage—which is still lower than Zlib. Lossy compression can also be disabled, or increased to reduce memory usage at the cost of quality. Changing this setting requires restarting the editor. |
Editor Settings
The available Editor settings are located under the Editor > Texture Import > Virtual Textures category in the Project Settings window.
|
Properties |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Auto Virtual Texturing Size |
Automatically enable the Virtual Texture Streaming texture setting for textures larger than or equal to this size. This setting will not affect existing textures in the project. |
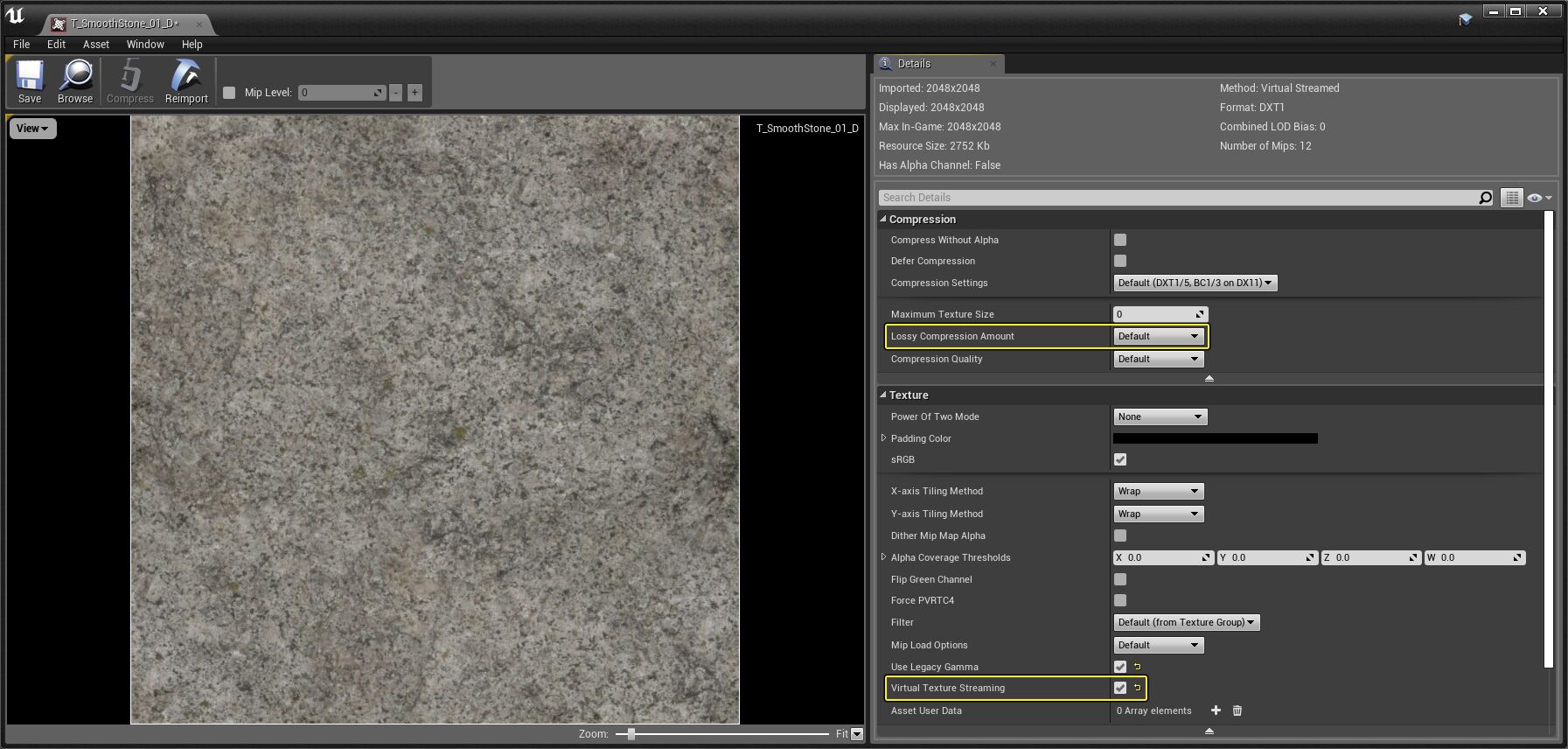
Texture Editor
Use the Texture Editor to set and control lossy compression amounts and whether a Texture supports SVT.
Click image for full size.
|
Properties |
Description |
|
|---|---|---|
|
Compression |
||
|
Lossy Compression Amount |
How aggressively any relevant lossy compression should be applied. use one of the available options, from lowest with no lossy compression at all, to the highest, which gives the worst image quality but with the smallest file size. |
|
|
Texture |
||
|
Virtual Texture Streaming |
Whether this texture should be streamed in using Virtual Texturing. Note that this parameter is enabled by default for any textures imported that are equal to or larger than the Auto Virtual Texturing Size set in the Project Settings under Editor > Virtual Texturing . |
|
Runtime Virtual Texture Settings
Use the following settings and properties to set up and work with Runtime Virtual Texturing in your project.
Runtime Virtual Texture Asset
When opening a Runtime Virtual Texture Asset, use this window to set parameters for the generated RVT in your scene with any Runtime Virtual Texture Volume that is referencing it. You can create an RVT Asset from the Add New menu under Materials & Textures .

|
Properties |
Description |
|
|---|---|---|
|
Details |
||
|
Page Table Texture Memory (estimated) |
Estimated page table texture memory that this Virtual Texture Asset is consuming. |
|
|
Physical Texture Memory (estimated) |
Estimated physical memory that this Virtual Texture Asset is consuming. |
|
|
Size |
||
|
Size of the virtual texture in tiles |
The size of this RVT in tiles. The final resolution of the RVT is this value multiplied by the Tile Size. A maximum of 4096 tiles is currently supported. This value is applied to the largest of either width or height from the associated RVT Volume. The size of the smaller axis will be chosen to match the aspect ratio of the RVT Volume. |
|
|
Size of each virtual texture tile |
The tile size used by this RVT. Virtual texture data is rendered and stored in tiles. Using a smaller tile size means that each tile is cheaper to generate, but more tiles need to be generated. |
|
|
Border padding for each virtual texture tile |
The number of padding texels used for each tile. A higher number has a small impact on memory and performance. A value of 0 will cause shading seams from bilinear sampling artifacts at tile edges. A value of 2 should fix this, and higher values are needed to enable anisotropic sampling. |
|
|
Layout |
||
|
Virtual texture content |
Choose what Material Attributes will be stored in this RVT:
This setting needs to match settings in the associated Material Assets for the RVT to work correctly. |
|
|
Enable BC texture compression |
Enables texture compression of the data stored in the RVT. This reduces memory cost by a factor of four to eight times, and improves sampling performance. Using uncompressed is only recommended for debugging and quality comparisons. |
|
|
Enable clear before render |
When this is set each tile is cleared before rendering to it. Disabling this can be an optimization if you know that the texture will always be fully covered by rendering. |
|
|
Enable packed page table |
When this is set the RVT uses an optimized page table setup. This reduces page table memory and update cost but can reduce the ability to share physical memory with other virtual textures. |
|
|
Enable private page table |
When this is set the RVT will allocate its page table resources individually instead of from a globally shared page table atlas. This can reduce total page table memory allocation but can also reduce the total number of virtual textures supported. |
|
|
Enable adaptive page table |
When this is set the RVT uses a sparse adaptive page table. This supports tile counts that are larger than the page table size. This in turn means that larger virtual texture resolutions are possible. There is a small performance cost when sampling an adaptive page table, so this should be set only when large tile counts are required. |
|
|
Enable continuous page updates |
When this is set the RVT will refresh some number pages each frame that have already been generated. The number is controlled by the r.VT.MaxContinuousUpdatesPerFrame CVar. Enabling this can provide a simple solution to visual problems caused when some RVT pages are generated before their dependent textures have been fully streamed. |
|
|
Low Mips to Remove |
The number of low mips to remove from this RVT. Low mips cover the most area and therefore can be the most expensive to render. Removing them can therefore improve performance. However, without the low mips available we can introduce mip shimmering artifacts in the final render. Using streaming low mips is usually a better alternative to this option. |
|
|
Texture Group |
Each RVT can belong to a LOD Texture Group that can be configured to override tile count or tile size per platform. |
|
Runtime Virtual Texture Sample Material Node Settings
The following properties are available on some of the Runtime Virtual Texture Material Expressions in the Material Editor.
|
Property |
Description |
|
|---|---|---|
|
|
||
|
Virtual Texture |
The Runtime Virtual Texture Asset to sample. |
|
|
Virtual Texture Content |
How to interpret the virtual texture contents. Note that the bound Virtual Texture Asset should have the same setting for sampling to work correctly. |
|
|
Enable packed page table |
Enable page table channel packing. Note that the bound Virtual Texture Asset should have the same setting for sampling to work correctly. |
|
|
Enable adaptive page table |
Enable sparse adaptive page table sampling. Note that the bound Virtual Texture Asset should have the same setting for sampling to work correctly. |
|
|
Texture Sample |
||
|
Mip Value Mode |
Defines how the Mip Value property on a Runtime Virtual Texture expression is applied to the virtual texture lookup.
Extreme settings here can have an impact on performance. For example, a large negative MipBias or forcing a MipLevel of 0 will require that more virtual texture pages need to be resident. This can cause thrashing of the physical pool |
|
Runtime Virtual Texture Volume
Use the Runtime Virtual Texture Volume to assign a Runtime Virtual Texture Asset to generate an RVT in your scene from Landscape Actors and scene Primitives that use the same RVT Asset.

|
Properties |
Description |
|
|---|---|---|
|
Virtual Texture |
||
|
Virtual Texture |
The Runtime Virtual Texture Asset to use. |
|
|
Scalability Group |
The Scalability Group to use for this RVT Volume. This selects which r.VT.RVT.TileCountBias.Group CVar will apply to the RVT set on this volume. |
|
|
Hide Primitives |
Enable this to hide associated primitives in the main pass. This will apply to all primitives that are set to render to the RVT on this volume and which have their "Draw in Main Pass" virtual texture setting set to "From Virtual Texture". |
|
|
Streaming Texture |
The Streaming Virtual Texture Asset to use for the low mips of this virtual texture. |
|
|
Enable Crunch |
Enables use of Crunch library to compress the Streaming Virtual Texture. Crunch is an open-source compression library designed to further compress GPU block-compressed textures (using DXT/BC/ETC compression). It makes data much smaller than Zlib, and decreases CPU cost to decompress. |
|
|
View Streaming Mips in Editor |
Enable this to show the Streaming Virtual Texture for the low mips when in editor. This is disabled by default because the Streaming Virtual Texture is only updated manually with the "Build" button and so can be out of sync during editing sessions. |
|
Actor Properties
Use the following settings and properties for scene Primitives and Landscapes.
Primitives
Settings and properties specific to the Actors in your scene.

|
Properties |
Description |
|
|---|---|---|
|
Virtual Texture |
||
|
Render to Virtual Textures |
An array of runtime virtual textures into which the mesh is rendered for the selected Actor. The Material also needs to be set up to output to a Virtual Texture. |
|
|
Draw in Main Pass |
Render to the main pass based on the selected virtual texture settings:
|
|
|
Virtual Texture LOD Bias |
Bias to the level of detail (LOD) selected for rendering to Runtime Virtual Textures. |
|
|
Virtual Texture Skip Mips |
The number of lower mips in the Runtime Virtual Texture to skip for rendering this primitive. Larger values reduce effective draw distance in the Runtime Virtual Texture. The culling method doesn't consider primitive size or virtual texture size. |
|
|
Virtual Texture Min Coverage |
Set the minimum pixel coverage before culling from the Runtime Virtual Texture. Larger values reduce the effective draw distance in the Runtime Virtual Texture. |
|
Landscape
Settings and properties specific to Landscape Actors in your scene.

|
Properties |
Description |
|
|---|---|---|
|
Virtual Texture |
||
|
Render to Virtual Textures |
An array of runtime virtual textures into which the mesh is rendered for the selected Actor. The Material also needs to be set up to output to a Virtual Texture. |
|
|
Virtual Texture Pass Type |
Render to the main pass based on the selected virtual texture settings:
|
|
|
Virtual Texture Num LODs |
Number of mesh levels to use when rendering Landscape into a runtime virtual texture. Set this value only if the Material used to render the virtual texture requires interpolated vertex data, such as height. Higher values use more tessellated meshes, and are expensive when rendering the runtime virtual texture. |
|
|
Virtual Texture LOD Bias |
Bias to the level of detail (LOD) selected for rendering to the runtime virtual textures. |
|
Landscape Splines
Settings and properties specific to Landscape Spline Actors in your scene.

|
Properties |
Description |
|
|---|---|---|
|
Virtual Texture |
||
|
Render to Virtual Textures |
An array of runtime virtual textures into which the mesh is rendered for the selected Actor. The Material also needs to be set up to output to a Virtual Texture. |
|
|
Virtual Texture Pass Type |
Render to the main pass based on the selected virtual texture settings:
|
|
|
Virtual Texture Num LODs |
Number of mesh levels to use when rendering Landscape into a runtime virtual texture. Set this value only if the Material used to render the virtual texture requires interpolated vertex data, such as height. Higher values use more tessellated meshes, and are expensive when rendering the runtime virtual texture. |
|
|
Virtual Texture LOD Bias |
Bias to the level of detail (LOD) selected for rendering to the runtime virtual textures. |
|
|
Virtual Texture Skip Mips |
The number of lower mips in the RVT to skip for rendering this primitive. Larger values reduce the effective draw distance in the RVT. This culling method doesn't consider primitive size or virtual texture size. |
|
|
Max Draw Distance in Main Pass |
The desired cull distance in the main pass if Draw in Main Pass is set to Always. A value of 0 has no effect. |
|