Choose your operating system:
Windows
macOS
Linux
Media Framework uses several assets to enable the playback of videos inside Unreal Engine 4 (UE4). Videos can be scrubbed, paused, or rewound inside a Media Player asset, as well as controlled through C++ or Blueprint Visual Scripting . Whether you want a surface in your Level playing a video, or you want to create a UI element with UMG to give players control over your video playback, you will first need to specify the Media Source so that the Engine can locate your media asset.
Media Source Types
There are several different Media Source assets that you can use to define where the media is coming from. Whether you have a file that is included as part of your project, streaming media from a website or using platform specific media, you will need to define a source before you can play the video. You can add a Media Source inside the Content Browser by clicking the Add New button, then under Media , specifying which source type you want to use.
File Media Source
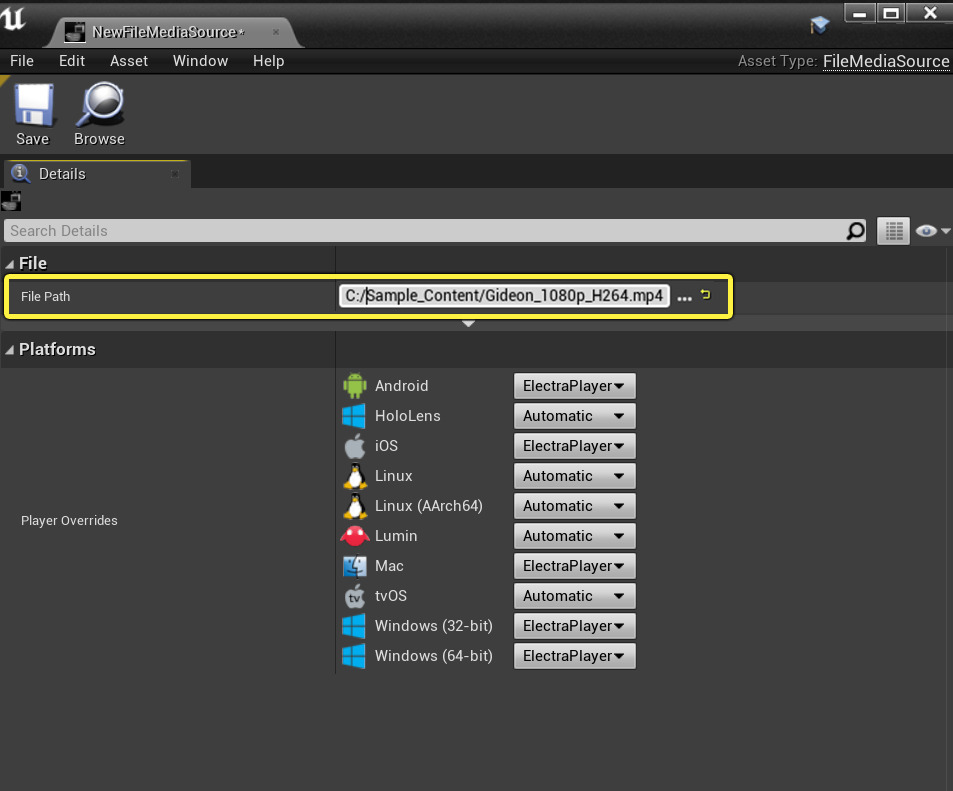
The File Media Source asset is used for media files stored on your device or in a shared local network file. The File Path section is where you specify where the media file resides.
While a media file can exist anywhere, it's typically a good practice to move your media files to the Content/Movies folder of your project and then point to the media file. This will ensure that your media is packaged correctly with your project. You will also see a yellow exclamation mark (as shown above) when pointing to a file outside of this location as a warning.
This type of source asset can load the entire media file into memory before playing by enabling the Precache File option (under the Advanced Options section). Based on the size of your file, caching time may vary, so take that into consideration when choosing this option. Each File Media Source asset can have its native Media Player Plugin (Plugin used to playback media) overridden on a per-platform basis (depicted below) or the player Plugin can be selected automatically.
Precaching may not be supported by all players and is currently only supported with MfMedia , PS4Media , and WmfMedia player Plugins.
Please see the Play a Video File how-to for working with File Media Source assets.
Image (Img) Media Source

The Img Media Source asset can be used for playback of image sequences stored on your device or from a shared local network where the Sequence Path field is used to point to the first image in your sequence. Images must be in a supported format and named sequentially (for example: MyImage01.exr or MyImage_01.exr ) in order for the Engine to discover and populate the remaining images in the sequence.
You can define a Frames Per Second Override and any Proxy Overrides for the images in your sequence as part of the advanced options. As with other source assets, you can define the player plugin to use based on the type of platform the media is playing on using the Player Overrides section.
Please see the Play an Image Sequence how-to for working with Img Media Source assets.
Stream Media Source

This Stream Media Source asset takes a URL as the source of your media and pulls it from the internet. Currently, linking to a YouTube or Dailymotion style URL is not supported, and you will need to link directly to a hosted file. Like the File Media Source asset, Stream Media Source assets can have their player Plugin overridden on a per-platform basis or the player Plugin can be selected automatically.
Please see the Play a Video Stream how-to for working with Stream Media Source assets.
Platform Media Source

The Platform Media Source asset supports overriding a Media Source on a per-platform basis. For example, suppose you want a particular video to play only on Android Devices or only on PS4. Inside the Media Sources section, you can designate which videos play on which platforms. When using a Platform Media Source, a Media Source must be selected for every platform.
Please see the Playing Platform Specific Media how-to for working with Platform Media Source assets.
Media Playlists
While you can play Media Source assets individually, the Media Playlist asset can play multiple Media Sources in order. After creating a few Media Source assets, you can add them to a Media Playlist, which will automatically cycle through and play each asset in the order you define. You can create Media Playlists inside the Content Browser from the Add New button under the Media section.
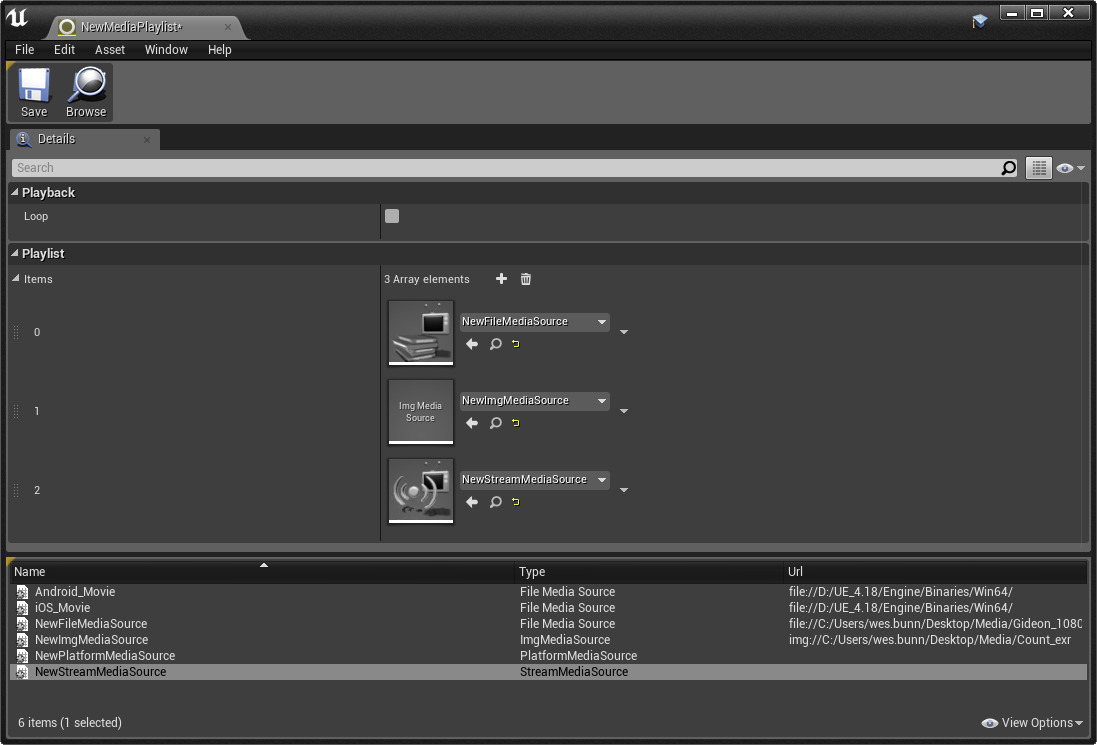
After creating and opening a Media Playlist, the Media Playlist Editor will open:
As of 4.18.1, the Loop option no longer loops the Playlist. In order to loop a Playlist, you can set the Loop option inside the Media Player asset.
In the Media Playlist Editor, you can define the source assets to include and specify the playback order. Any Media Source assets you have created will be displayed in the lower Media Library window which you can double-click on to add to the end of the playlist (or add by using the + button under the Items section.) Media Playlists can use a mixture of each Media Source type and play in order unless specified through Blueprint Script.
Please see the Using Media Playlists how-to for working with Media Playlist assets.
Media Sound Component
In order to hear audio associated with a video, you will need to create a Media Sound component and add it to your Blueprint or Actor playing back the media in your Level.
Prior to Engine version 4.18, a Media Sound Wave asset was used to generate sound and is now deprecated. If you are currently using these, you will need to delete them from your Level and associate a Media Sound component and assigned Media Player in order to generate audio with your videos.
Below we have a Static Mesh Actor in our Level, and in the Details panel have added a Media Sound component.
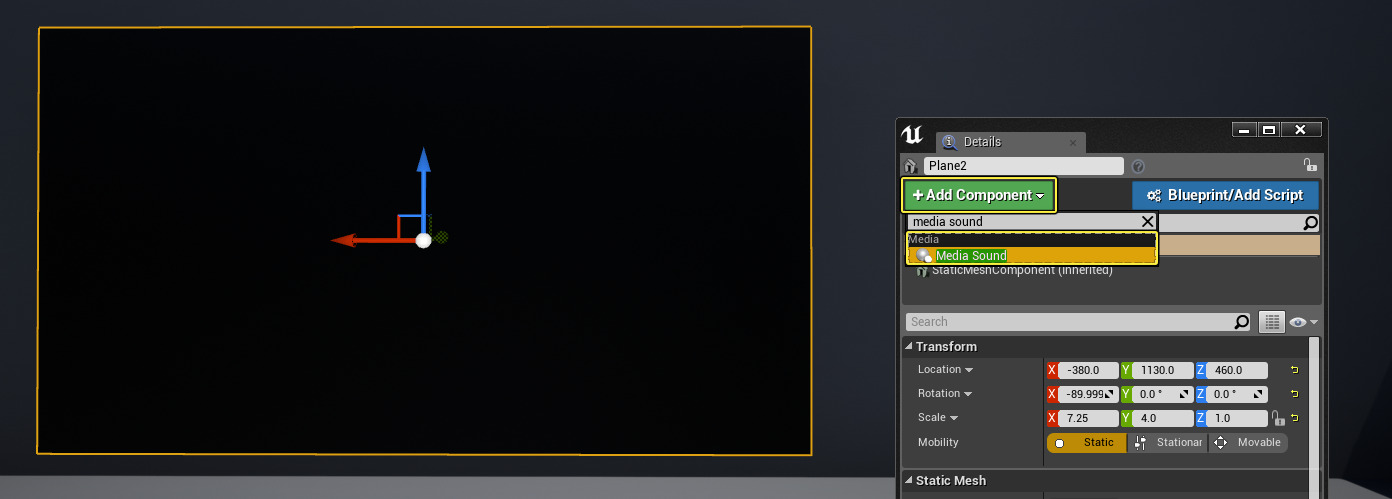
Once you have a Media Sound component added to your Actor or Blueprint, you will need to point the Media Sound component to a Media Player asset.
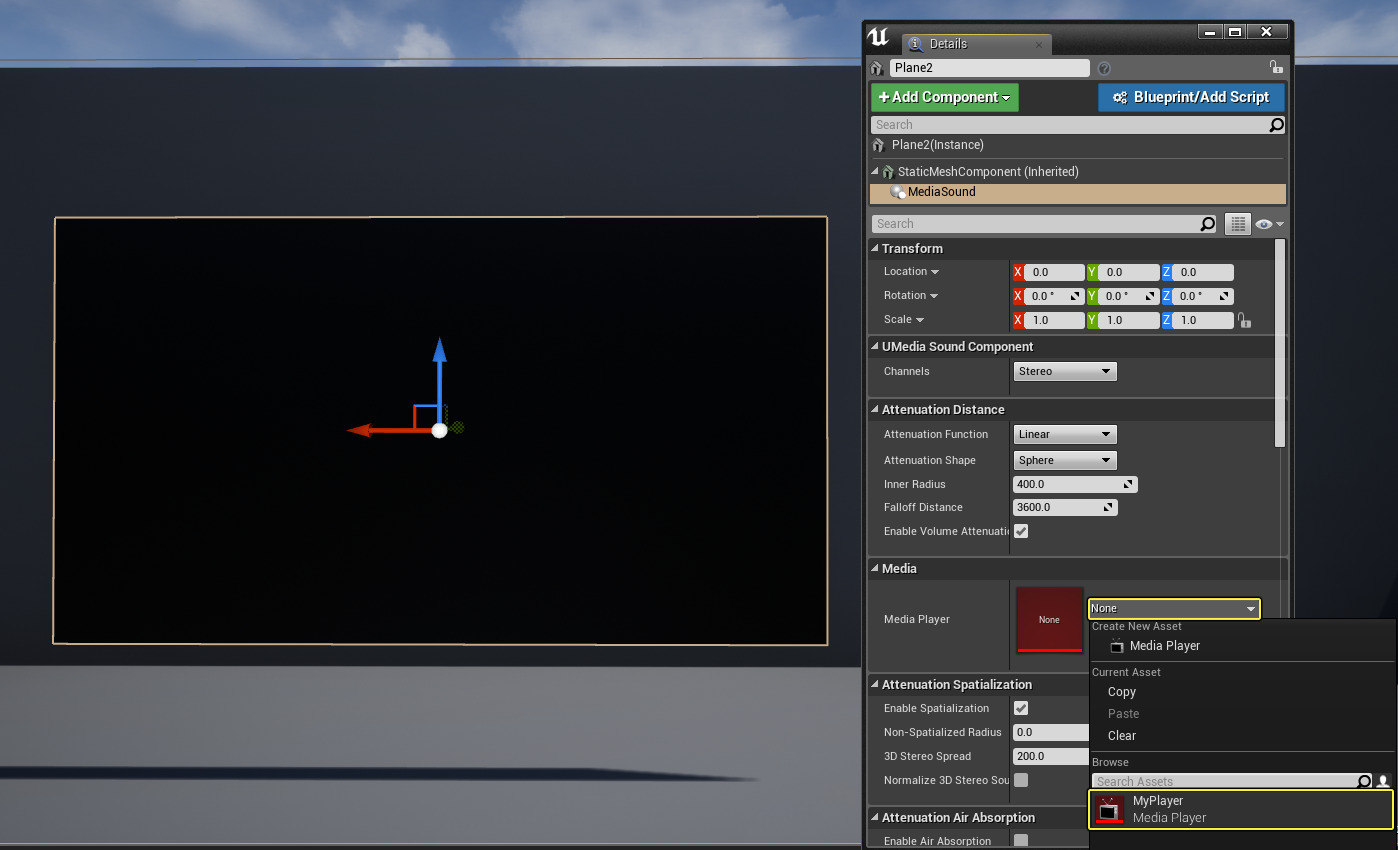
The Media Sound component provides Channels , Attenuation , Concurrency and other audio related settings inside the Details panel that you can use to define how your sound is perceived. When linked to a Media Player asset, audio attached to a video source will automatically playback along with the video. Typically, you can leave the default settings for the Media Sound component. However, if you need more control over the sound, you can adjust the Concurrency, Attenuation, and other settings.
The Surround channel setting currently is not supported by the audio mixer at this time and is slated for updates in a future Engine release.
Media Textures
Media Texture assets are used for rendering video tracks from Media Player assets.
While the Media Sound component provides the audio, Media Textures provide the visuals from your Media Source assets. Media Texture assets can be included within Materials that can then be applied to meshes in your levels such as a billboard, TV or monitor to make it appear as if the video is playing on that object within the game world. When you create a Media Texture asset, you will need to define which Media Player it is to reference inside the Details panel under Media Player .

Below, a Material including a Media Texture asset has been created and applied to a static mesh in the Level. Inside the Texture Editor , the Media Texture displays the same playback position as it appears in the Material in the Level. In addition to the standard Texture Properties available, Media Textures accept X and Y Axis Addressing values of Clamped , Mirror or World values.

Materials use a Texture Sample node which references the Media Texture asset. On the Texture Sample node, the Sampler Type property should be set to External unless you are using the Electra Media Player , then you must set the Sampler Type property to Color .
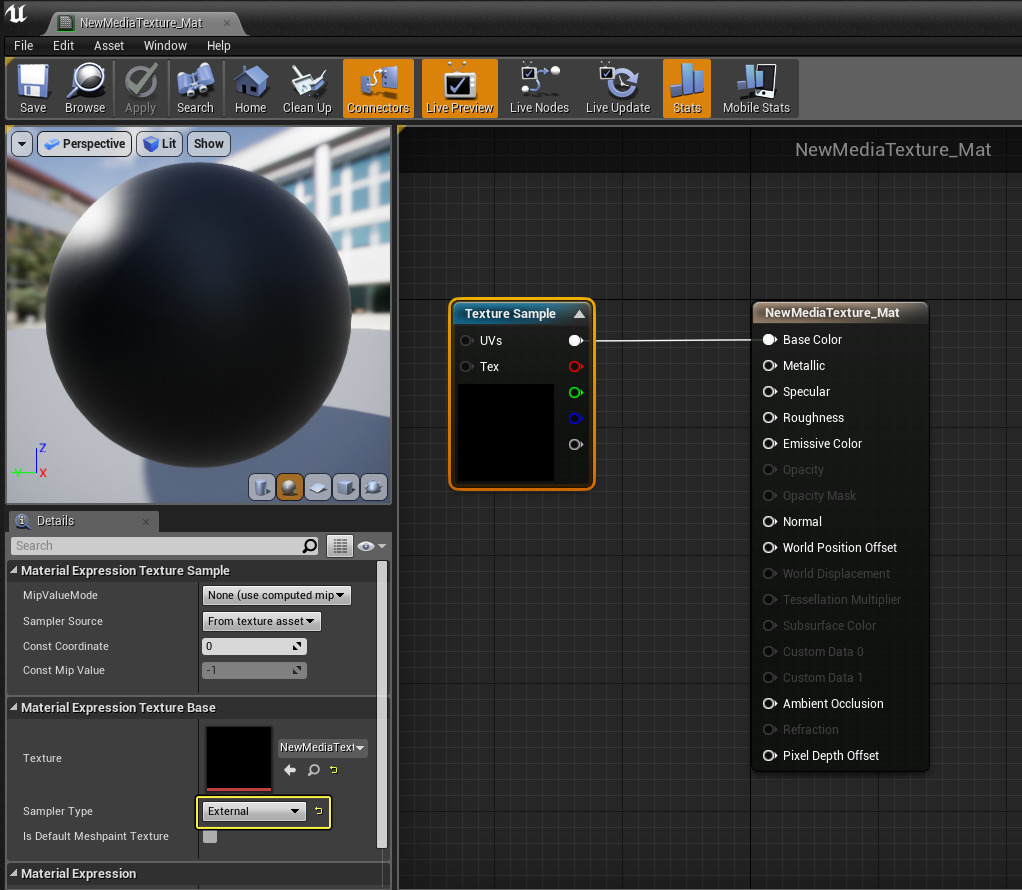
Default Sampler Type property setting.

Sampler Type property setting for the Electra Media Player
Materials that use a Media Texture created prior to Engine 4.18 may need to have the Sampler Type property manually set to External .
Media Player Assets
Once you have a Media Source or Media Playlist, you can play the asset using a Media Player asset. The Media Player asset requires the use of a Media Texture to produce the video playback and a Media Sound component to produce the audio associated with the video. You can create Media Player assets inside the Content Browser from the Add New Button under the Media section.

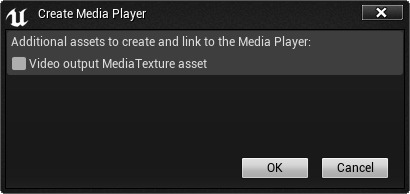
When creating Media Player assets, the Create Media Player window (pictured below) will appear asking if you would also like to create and link assets to the Media Player. This allows you to automatically create and assign a Media Texture associated with the Media Player asset you are creating.
Double-clicking on a Media Player asset will open the Media Player Editor :
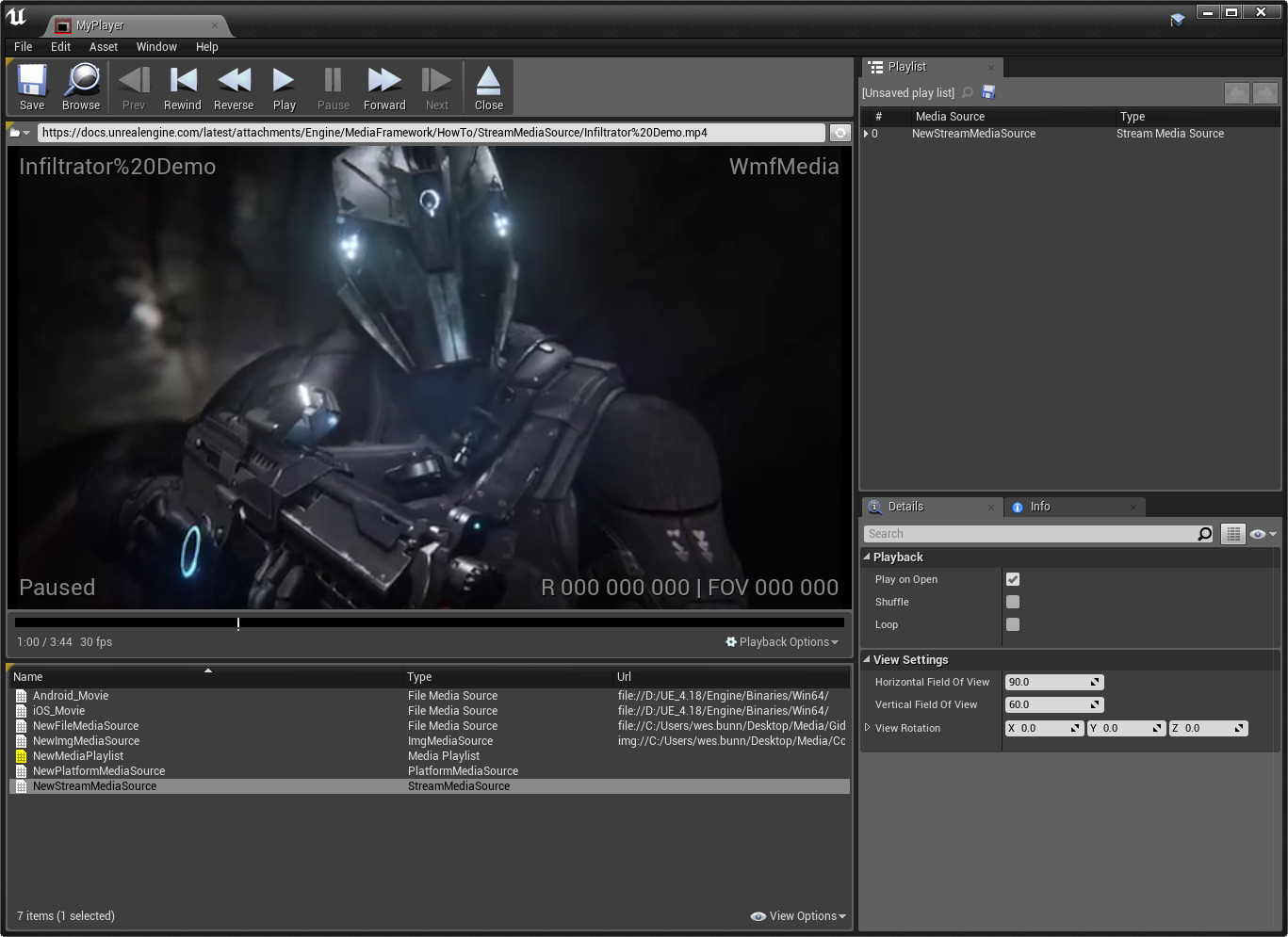
In the Media Player Editor, you can preview all the Media Source assets in your project, you can play, pause, rewind, or fast-forward (if supported) through media. You can also define playback settings for the Media Player asset including: where the media should automatically start playing when opened, whether the media should loop playback (if supported), or (if a playlist is being used) whether to shuffle and randomly select a source to play from the playlist.
For a more detailed breakdown of the Media Editor and options, please see the Media Editor Reference documentation page.
Media Assets & Scripting
Once your Media Player asset is set up and linked with a Media Texture and (if the video has audio) a Media Sound component, it can be played during a game session. In order to play media in-game, you will first need to create a reference to the Media Player asset through Blueprint or C++. To do this, create a Variable of the Media Player variable type inside any Blueprint and set the Default Value of the variable to reference your desired Media Player.

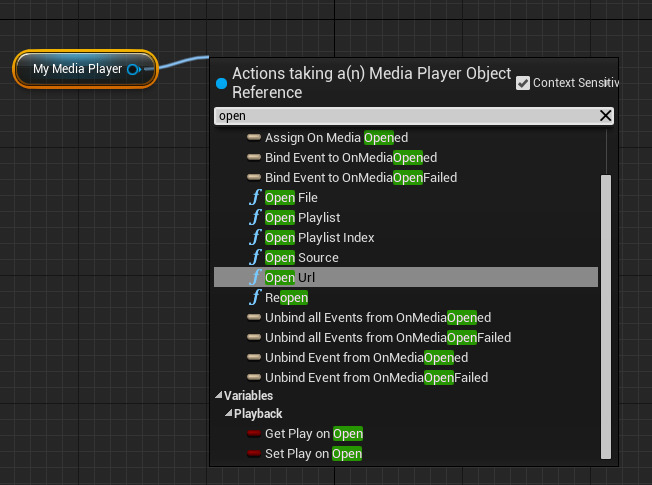
With a reference to your Media Player defined, you can then call an Open function based on the type of media source.
|
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Open File |
Opens a media file at the specified file location on your computer. |
|
Open Playlist |
Opens the first media source in the specified playlist. |
|
Open Playlist Index |
Opens a specific media source within a specified playlist. |
|
Open Source |
Opens the specified media source (File Media, Stream Media or Platform Media). |
|
Open URL |
Opens the specified media URL. |
|
Reopen |
Reopens the currently opened media or playlist. |
Newly created Media Player assets have the Play on Open option enabled by default which means when you open a Media Source it will start playing the video automatically. You can uncheck this option inside your Media Player asset to have the source avoid playing when open and only start playing when explicitly called through Blueprint or C++.
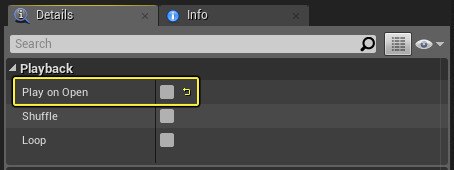
If you do not want to automatically play the media once it has been opened successfully, you can also hook into the Play Blueprint event.
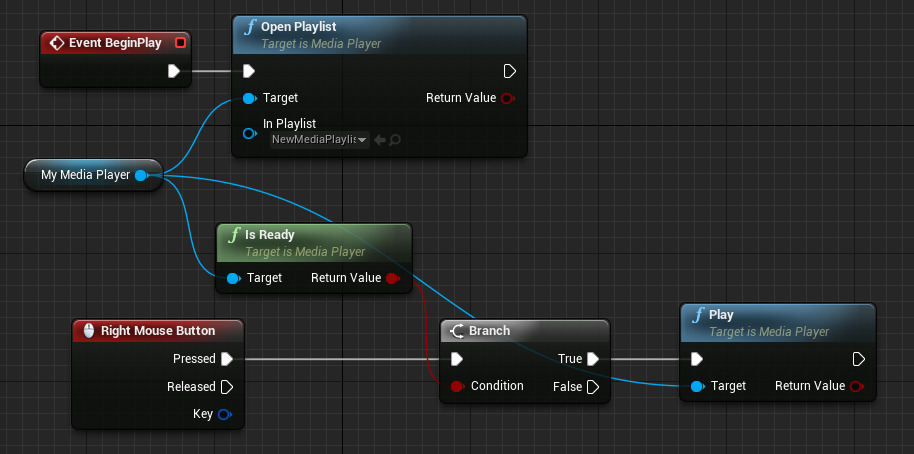
Above on Event BeginPlay , we open a Media Playlist and play the Media Player when the Right Mouse Button is Pressed only if it is ready to be played.
If you are not automatically playing a Media Source on open and are using the Play function to start playback, it is advised that you do not chain the Play call directly after an Open Source or Open Playlist call. This is because it may take some time for the Media Source to open and the Play command will just return false and the movie will not play as expected. In these instances, you may want to use a binding event that is bound to the On Media Opened call.
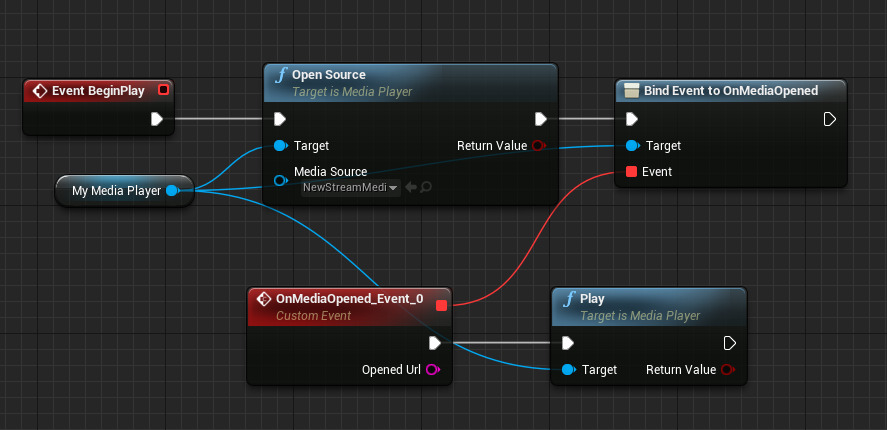
Above, we open a Stream Media source and bind the Media Player to On Media Opened which will fire an event when fully opened that will play the media.
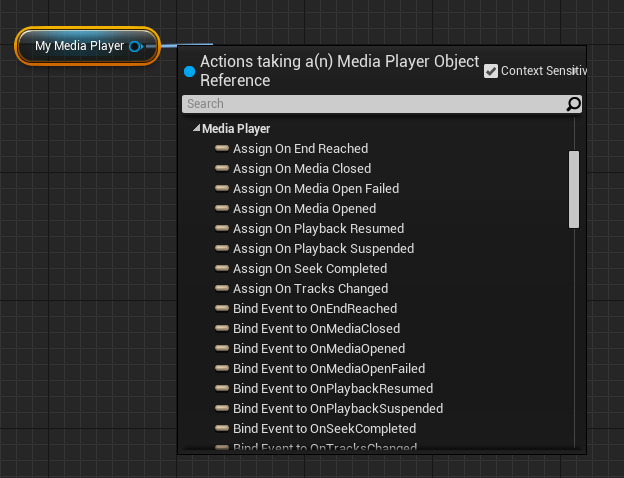
You can bind other functions with a Media Player reference to various states of playback (for example: if the video is paused or if the video ends). You can also call several different functions off a Media Player reference like checking if a video can be paused, checking if a video is playing, if a video set to loop, and accessing play rate information (among other use cases). To see these options, drag off a Media Player reference then look under the Media Player section of the Blueprint Context Menu.
Sequencer Integration
Playback of videos with Media Framework will be frame-accurately synced to the timeline in Sequencer independently of the media player's real-time behavior. Sequencer internally handles communication and setup for this synchronization with the media player.
Currently, only ImageMediaPlayer supports this new synchronization. If you use a media player that doesn't support this feature, playback will start or stop close to what is indicated by the Sequencer timeline; however, frame-by-frame alignment could be random.