UDN
Search public documentation:
DevelopmentKitGemsCreatingAMouseInterface
日本語訳
中国翻译
한국어
Interested in the Unreal Engine?
Visit the Unreal Technology site.
Looking for jobs and company info?
Check out the Epic games site.
Questions about support via UDN?
Contact the UDN Staff
中国翻译
한국어
Interested in the Unreal Engine?
Visit the Unreal Technology site.
Looking for jobs and company info?
Check out the Epic games site.
Questions about support via UDN?
Contact the UDN Staff
UE3 Home > Unreal Development Kit Gems > Creating a mouse interface
UE3 Home > User Interfaces & HUDs > Creating a mouse interface
UE3 Home > User Interfaces & HUDs > Creating a mouse interface
Creating a mouse interface
Last tested against UDK Apr, 2011
PC compatible
Overview
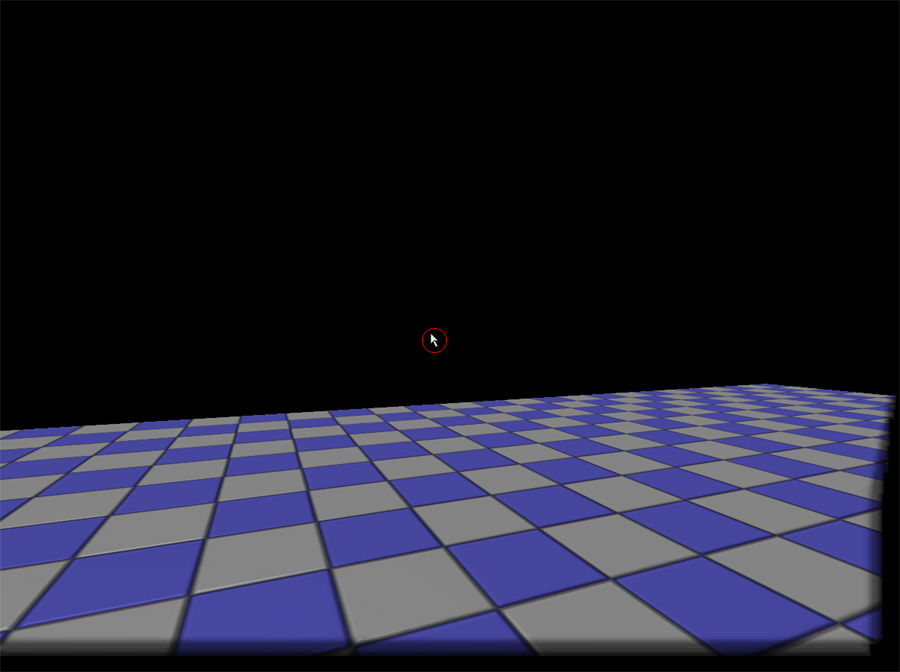
Getting a cursor on the screen
Unrealscript
It is possible to create your own mouse positioning code. This is done by adding a custom player input which polls aMouseX and aMouseY to see if there has been any changes. If there has been a change, it is appended to the MousePosition variable and then clamped to keep the mouse cursor within the screen bounds. This is the new game info. It is a simple GameInfo which defines the HUD class and PlayerController class to use.
class MouseInterfaceGameInfo extends GameInfo;
defaultproperties
{
// Set the HUD type to the mouse interface HUD
HUDType=class'MouseInterfaceHUD'
// Set the player controller to the mouse interface Player Controller
PlayerControllerClass=class'MouseInterfacePlayerController'
}
class MouseInterfaceHUD extends HUD;
// The texture which represents the cursor on the screen
var const Texture2D CursorTexture;
// The color of the cursor
var const Color CursorColor;
event PostRender()
{
local MouseInterfacePlayerInput MouseInterfacePlayerInput;
// Ensure that we have a valid PlayerOwner and CursorTexture
if (PlayerOwner != None && CursorTexture != None)
{
// Cast to get the MouseInterfacePlayerInput
MouseInterfacePlayerInput = MouseInterfacePlayerInput(PlayerOwner.PlayerInput);
if (MouseInterfacePlayerInput != None)
{
// Set the canvas position to the mouse position
Canvas.SetPos(MouseInterfacePlayerInput.MousePosition.X, MouseInterfacePlayerInput.MousePosition.Y);
// Set the cursor color
Canvas.DrawColor = CursorColor;
// Draw the texture on the screen
Canvas.DrawTile(CursorTexture, CursorTexture.SizeX, CursorTexture.SizeY, 0.f, 0.f, CursorTexture.SizeX, CursorTexture.SizeY,, true);
}
}
Super.PostRender();
}
defaultproperties
{
CursorColor=(R=255,G=255,B=255,A=255)
CursorTexture=Texture2D'EngineResources.Cursors.Arrow'
}
- When PostRender is executed we get the new PlayerInput from the PlayerOwner, which is a PlayerController.
- If we have our new PlayerInput, we then set the Canvas position to the MousePosition stored inside our new PlayerInput.
- We then set the color to the cursor color defined in the default properties.
- Finally, we draw the texture which represents the mouse cursor.
class MouseInterfacePlayerController extends PlayerController;
// Null this function
function UpdateRotation(float DeltaTime);
defaultproperties
{
// Set the input class to the mouse interface player input
InputClass=class'MouseInterfacePlayerInput'
}
class MouseInterfacePlayerInput extends PlayerInput;
// Stored mouse position. Set to private write as we don't want other classes to modify it, but still allow other classes to access it.
var PrivateWrite IntPoint MousePosition;
event PlayerInput(float DeltaTime)
{
// Handle mouse
// Ensure we have a valid HUD
if (myHUD != None)
{
// Add the aMouseX to the mouse position and clamp it within the viewport width
MousePosition.X = Clamp(MousePosition.X + aMouseX, 0, myHUD.SizeX);
// Add the aMouseY to the mouse position and clamp it within the viewport height
MousePosition.Y = Clamp(MousePosition.Y - aMouseY, 0, myHUD.SizeY);
}
Super.PlayerInput(DeltaTime);
}
defaultproperties
{
}
- When PlayerInput is executed, we handle adjust the mouse position.
- The HUD is required to clamp the mouse position within the viewport. As the PlayerInput is an object within the PlayerController, we can access the variable within the PlayerController directly.
- Using aMouseX and aMouseY which is bound within the input config, we add those values to our MousePosition variable. We have to inverse the vertical calculations to produce the right results.
- By clamping the results, we make sure that the mouse position always stays within the viewport.
ScaleForm
ScaleForm can also be used to poll for the mouse position. In this particular gem, the majority of the scripts stay largely the same. The exception is, is if you use ScaleForm, the custom player input class created above no longer polls for mouse changes. Instead, when ScaleForm detects a change in the mouse position, it will pass the new mouse position to Unrealscript. This is the action script written in Adobe Flash. When the mouse moves, action script sets the position of a layer called cursor to the ScaleForm's mouse position and it also sends Unrealscript ScaleForm's mouse position.
import flash.external.ExternalInterface;
// Hide normal "Windows" pointer.
Mouse.hide();
var mouseListener:Object = new Object();
mouseListener.onMouseMove = function() {
// Set the cursor instance position to the mouse position.
cursor._x = _root._xmouse;
cursor._y = _root._ymouse;
// Pass Unrealscript the new mouse coordinates
ExternalInterface.call("UpdateMousePosition", _root._xmouse, _root._ymouse);
updateAfterEvent();
};
Mouse.addListener(mouseListener);
class MouseInterfaceGFx extends GFxMoviePlayer;
var MouseInterfaceHUD MouseInterfaceHUD;
function Init(optional LocalPlayer LocalPlayer)
{
// Initialize the ScaleForm movie
Super.Init(LocalPlayer);
Start();
Advance(0);
}
event UpdateMousePosition(float X, float Y)
{
local MouseInterfacePlayerInput MouseInterfacePlayerInput;
if (MouseInterfaceHUD != None && MouseInterfaceHUD.PlayerOwner != None)
{
MouseInterfacePlayerInput = MouseInterfacePlayerInput(MouseInterfaceHUD.PlayerOwner.PlayerInput);
if (MouseInterfacePlayerInput != None)
{
MouseInterfacePlayerInput.SetMousePosition(X, Y);
}
}
}
defaultproperties
{
bDisplayWithHudOff=false
TimingMode=TM_Game
MovieInfo=SwfMovie'MouseInterfaceContent.MouseInterfaceCursor'
bPauseGameWhileActive=false
}
class MouseInterfaceHUD extends HUD;
// The texture which represents the cursor on the screen
var const Texture2D CursorTexture;
// The color of the cursor
var const Color CursorColor;
// Use ScaleForm?
var bool UsingScaleForm;
// Scaleform mouse movie
var MouseInterfaceGFx MouseInterfaceGFx;
simulated event PostBeginPlay()
{
Super.PostBeginPlay();
// If we are using ScaleForm, then create the ScaleForm movie
if (UsingScaleForm)
{
MouseInterfaceGFx = new () class'MouseInterfaceGFx';
if (MouseInterfaceGFx != None)
{
MouseInterfaceGFx.MouseInterfaceHUD = Self;
MouseInterfaceGFx.SetTimingMode(TM_Game);
MouseInterfaceGFx.Init(class'Engine'.static.GetEngine().GamePlayers[MouseInterfaceGFx.LocalPlayerOwnerIndex]);
}
}
}
simulated event Destroyed()
{
Super.Destroyed();
// If the ScaleForm movie exists, then destroy it
if (MouseInterfaceGFx != None)
{
MouseInterfaceGFx.Close(true);
MouseInterfaceGFx = None;
}
}
function PreCalcValues()
{
Super.PreCalcValues();
// If the ScaleForm movie exists, then reset it's viewport, scale mode and alignment to match the
// screen resolution
if (MouseInterfaceGFx != None)
{
MouseInterfaceGFx.SetViewport(0, 0, SizeX, SizeY);
MouseInterfaceGFx.SetViewScaleMode(SM_NoScale);
MouseInterfaceGFx.SetAlignment(Align_TopLeft);
}
}
event PostRender()
{
local MouseInterfacePlayerInput MouseInterfacePlayerInput;
local MouseInterfaceInteractionInterface MouseInteractionInterface;
local Vector HitLocation, HitNormal;
Super.PostRender();
// Ensure that we aren't using ScaleForm and that we have a valid cursor
if (!UsingScaleForm && CursorTexture != None)
{
// Ensure that we have a valid PlayerOwner
if (PlayerOwner != None)
{
// Cast to get the MouseInterfacePlayerInput
MouseInterfacePlayerInput = MouseInterfacePlayerInput(PlayerOwner.PlayerInput);
// If we're not using scale form and we have a valid cursor texture, render it
if (MouseInterfacePlayerInput != None)
{
// Set the canvas position to the mouse position
Canvas.SetPos(MouseInterfacePlayerInput.MousePosition.X, MouseInterfacePlayerInput.MousePosition.Y);
// Set the cursor color
Canvas.DrawColor = CursorColor;
// Draw the texture on the screen
Canvas.DrawTile(CursorTexture, CursorTexture.SizeX, CursorTexture.SizeY, 0.f, 0.f, CursorTexture.SizeX, CursorTexture.SizeY,, true);
}
}
}
Super.PostRender();
}
class MouseInterfacePlayerInput extends PlayerInput;
var PrivateWrite IntPoint MousePosition;
event PlayerInput(float DeltaTime)
{
local MouseInterfaceHUD MouseInterfaceHUD;
// Handle mouse movement
// Check that we have the appropriate HUD class
MouseInterfaceHUD = MouseInterfaceHUD(MyHUD);
if (MouseInterfaceHUD != None)
{
if (!MouseInterfaceHUD.UsingScaleForm)
{
// If we are not using ScaleForm, then read the mouse input directly
// Add the aMouseX to the mouse position and clamp it within the viewport width
MousePosition.X = Clamp(MousePosition.X + aMouseX, 0, MouseInterfaceHUD.SizeX);
// Add the aMouseY to the mouse position and clamp it within the viewport height
MousePosition.Y = Clamp(MousePosition.Y - aMouseY, 0, MouseInterfaceHUD.SizeY);
}
}
Super.PlayerInput(DeltaTime);
}
function SetMousePosition(int X, int Y)
{
if (MyHUD != None)
{
MousePosition.X = Clamp(X, 0, MyHUD.SizeX);
MousePosition.Y = Clamp(Y, 0, MyHUD.SizeY);
}
}
defaultproperties
{
}
Related Topics
I just want the mouse 2D coordinates!
To retrieve the mouse 2D coordinates, you just need access to the MouseInterfacePlayerInput. To retrieve it from within the HUD.
local MouseInterfacePlayerInput MouseInterfacePlayerInput;
local IntPoint MousePosition;
// Ensure that we have a valid PlayerOwner
if (PlayerOwner != None)
{
// Cast to get the MouseInterfacePlayerInput
MouseInterfacePlayerInput = MouseInterfacePlayerInput(PlayerOwner.PlayerInput);
if (MouseInterfacePlayerInput != None)
{
// To retrieve/use the mouse X position
MousePosition.X = MouseInterfacePlayerInput.MousePosition.X;
// To retrieve/use the mouse Y position
MousePosition.Y = MouseInterfacePlayerInput.MousePosition.Y;
}
}
local MouseInterfacePlayerInput MouseInterfacePlayerInput;
local IntPoint MousePosition;
// Cast to get the MouseInterfacePlayerInput
MouseInterfacePlayerInput = MouseInterfacePlayerInput(PlayerInput);
if (MouseInterfacePlayerInput != None)
{
// To retrieve/use the mouse X position
MousePosition.X = MouseInterfacePlayerInput.MousePosition.X;
// To retrieve/use the mouse Y position
MousePosition.Y = MouseInterfacePlayerInput.MousePosition.Y;
}
Related topics
Adding the mouse interaction interface
interface MouseInterfaceInteractionInterface; // Called when the left mouse button is pressed function MouseLeftPressed(Vector MouseWorldOrigin, Vector MouseWorldDirection, Vector HitLocation, Vector HitNormal); // Called when the left mouse button is released function MouseLeftReleased(Vector MouseWorldOrigin, Vector MouseWorldDirection); // Called when the right mouse button is pressed function MouseRightPressed(Vector MouseWorldOrigin, Vector MouseWorldDirection, Vector HitLocation, Vector HitNormal); // Called when the right mouse button is released function MouseRightReleased(Vector MouseWorldOrigin, Vector MouseWorldDirection); // Called when the middle mouse button is pressed function MouseMiddlePressed(Vector MouseWorldOrigin, Vector MouseWorldDirection, Vector HitLocation, Vector HitNormal); // Called when the middle mouse button is released function MouseMiddleReleased(Vector MouseWorldOrigin, Vector MouseWorldDirection); // Called when the middle mouse button is scrolled up function MouseScrollUp(Vector MouseWorldOrigin, Vector MouseWorldDirection); // Called when the middle mouse button is scrolled down function MouseScrollDown(Vector MouseWorldOrigin, Vector MouseWorldDirection); // Called when the mouse is moved over the actor function MouseOver(Vector MouseWorldOrigin, Vector MouseWorldDirection); // Called when the mouse is moved out from the actor (when it was previously over it) function MouseOut(Vector MouseWorldOrigin, Vector MouseWorldDirection); // Returns the hit location of the mouse trace function Vector GetHitLocation(); // Returns the hit normal of the mouse trace function Vector GetHitNormal(); // Returns the mouse world origin calculated by the deprojection within the canvas function Vector GetMouseWorldOrigin(); // Returns the mouse world direction calculated by the deprojection within the canvas function Vector GetMouseWorldDirection();
Related topics
Using the PlayerController and HUD to provide the mouse interaction
class MouseInterfacePlayerController extends PlayerController;
// Mouse event enum
enum EMouseEvent
{
LeftMouseButton,
RightMouseButton,
MiddleMouseButton,
ScrollWheelUp,
ScrollWheelDown,
};
// Handle mouse inputs
function HandleMouseInput(EMouseEvent MouseEvent, EInputEvent InputEvent)
{
local MouseInterfaceHUD MouseInterfaceHUD;
// Type cast to get our HUD
MouseInterfaceHUD = MouseInterfaceHUD(myHUD);
if (MouseInterfaceHUD != None)
{
// Detect what kind of input this is
if (InputEvent == IE_Pressed)
{
// Handle pressed event
switch (MouseEvent)
{
case LeftMouseButton:
MouseInterfaceHUD.PendingLeftPressed = true;
break;
case RightMouseButton:
MouseInterfaceHUD.PendingRightPressed = true;
break;
case MiddleMouseButton:
MouseInterfaceHUD.PendingMiddlePressed = true;
break;
case ScrollWheelUp:
MouseInterfaceHUD.PendingScrollUp = true;
break;
case ScrollWheelDown:
MouseInterfaceHUD.PendingScrollDown = true;
break;
default:
break;
}
}
else if (InputEvent == IE_Released)
{
// Handle released event
switch (MouseEvent)
{
case LeftMouseButton:
MouseInterfaceHUD.PendingLeftReleased = true;
break;
case RightMouseButton:
MouseInterfaceHUD.PendingRightReleased = true;
break;
case MiddleMouseButton:
MouseInterfaceHUD.PendingMiddleReleased = true;
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
}
// Hook used for the left and right mouse button when pressed
exec function StartFire(optional byte FireModeNum)
{
HandleMouseInput((FireModeNum == 0) ? LeftMouseButton : RightMouseButton, IE_Pressed);
Super.StartFire(FireModeNum);
}
// Hook used for the left and right mouse button when released
exec function StopFire(optional byte FireModeNum)
{
HandleMouseInput((FireModeNum == 0) ? LeftMouseButton : RightMouseButton, IE_Released);
Super.StopFire(FireModeNum);
}
// Called when the middle mouse button is pressed
exec function MiddleMousePressed()
{
HandleMouseInput(MiddleMouseButton, IE_Pressed);
}
// Called when the middle mouse button is released
exec function MiddleMouseReleased()
{
HandleMouseInput(MiddleMouseButton, IE_Released);
}
// Called when the middle mouse wheel is scrolled up
exec function MiddleMouseScrollUp()
{
HandleMouseInput(ScrollWheelUp, IE_Pressed);
}
// Called when the middle mouse wheel is scrolled down
exec function MiddleMouseScrollDown()
{
HandleMouseInput(ScrollWheelDown, IE_Pressed);
}
// Null this function
function UpdateRotation(float DeltaTime);
// Override this state because StartFire isn't called globally when in this function
auto state PlayerWaiting
{
exec function StartFire(optional byte FireModeNum)
{
Global.StartFire(FireModeNum);
}
}
defaultproperties
{
// Set the input class to the mouse interface player input
InputClass=class'MouseInterfacePlayerInput'
}
- Exec functions are called via key binds.
- If any of the exec functions are called, they then call HandleMouseInput which then defers the action to the HUD.
; Remove the previous mouse scroll up and scroll down key binds -Bindings=(Name="MouseScrollUp",Command="PrevWeapon") -Bindings=(Name="MouseScrollDown",Command="NextWeapon") ; Add the middle mouse button and new scroll wheel key binds .Bindings=(Name="MiddleMouseButton",Command="MiddleMousePressed | OnRelease MiddleMouseReleased") .Bindings=(Name="MouseScrollUp",Command="GBA_PrevWeapon | MiddleMouseScrollUp") .Bindings=(Name="MouseScrollDown",Command="GBA_NextWeapon | MiddleMouseScrollDown")
class MouseInterfaceHUD extends HUD;
// The texture which represents the cursor on the screen
var const Texture2D CursorTexture;
// The color of the cursor
var const Color CursorColor;
// Pending left mouse button pressed event
var bool PendingLeftPressed;
// Pending left mouse button released event
var bool PendingLeftReleased;
// Pending right mouse button pressed event
var bool PendingRightPressed;
// Pending right mouse button released event
var bool PendingRightReleased;
// Pending middle mouse button pressed event
var bool PendingMiddlePressed;
// Pending middle mouse button released event
var bool PendingMiddleReleased;
// Pending mouse wheel scroll up event
var bool PendingScrollUp;
// Pending mouse wheel scroll down event
var bool PendingScrollDown;
// Cached mouse world origin
var Vector CachedMouseWorldOrigin;
// Cached mouse world direction
var Vector CachedMouseWorldDirection;
// Last mouse interaction interface
var MouseInterfaceInteractionInterface LastMouseInteractionInterface;
// Use ScaleForm?
var bool UsingScaleForm;
// Scaleform mouse movie
var MouseInterfaceGFx MouseInterfaceGFx;
simulated event PostBeginPlay()
{
Super.PostBeginPlay();
// If we are using ScaleForm, then create the ScaleForm movie
if (UsingScaleForm)
{
MouseInterfaceGFx = new () class'MouseInterfaceGFx';
if (MouseInterfaceGFx != None)
{
MouseInterfaceGFx.MouseInterfaceHUD = Self;
MouseInterfaceGFx.SetTimingMode(TM_Game);
MouseInterfaceGFx.Init(class'Engine'.static.GetEngine().GamePlayers[MouseInterfaceGFx.LocalPlayerOwnerIndex]);
}
}
}
simulated event Destroyed()
{
Super.Destroyed();
// If the ScaleForm movie exists, then destroy it
if (MouseInterfaceGFx != None)
{
MouseInterfaceGFx.Close(true);
MouseInterfaceGFx = None;
}
}
function PreCalcValues()
{
Super.PreCalcValues();
// If the ScaleForm movie exists, then reset it's viewport, scale mode and alignment to match the
// screen resolution
if (MouseInterfaceGFx != None)
{
MouseInterfaceGFx.SetViewport(0, 0, SizeX, SizeY);
MouseInterfaceGFx.SetViewScaleMode(SM_NoScale);
MouseInterfaceGFx.SetAlignment(Align_TopLeft);
}
}
event PostRender()
{
local MouseInterfacePlayerInput MouseInterfacePlayerInput;
local MouseInterfaceInteractionInterface MouseInteractionInterface;
local Vector HitLocation, HitNormal;
Super.PostRender();
// Ensure that we aren't using ScaleForm and that we have a valid cursor
if (!UsingScaleForm && CursorTexture != None)
{
// Ensure that we have a valid PlayerOwner
if (PlayerOwner != None)
{
// Cast to get the MouseInterfacePlayerInput
MouseInterfacePlayerInput = MouseInterfacePlayerInput(PlayerOwner.PlayerInput);
// If we're not using scale form and we have a valid cursor texture, render it
if (MouseInterfacePlayerInput != None)
{
// Set the canvas position to the mouse position
Canvas.SetPos(MouseInterfacePlayerInput.MousePosition.X, MouseInterfacePlayerInput.MousePosition.Y);
// Set the cursor color
Canvas.DrawColor = CursorColor;
// Draw the texture on the screen
Canvas.DrawTile(CursorTexture, CursorTexture.SizeX, CursorTexture.SizeY, 0.f, 0.f, CursorTexture.SizeX, CursorTexture.SizeY,, true);
}
}
}
// Get the current mouse interaction interface
MouseInteractionInterface = GetMouseActor(HitLocation, HitNormal);
// Handle mouse over and mouse out
// Did we previously had a mouse interaction interface?
if (LastMouseInteractionInterface != None)
{
// If the last mouse interaction interface differs to the current mouse interaction
if (LastMouseInteractionInterface != MouseInteractionInterface)
{
// Call the mouse out function
LastMouseInteractionInterface.MouseOut(CachedMouseWorldOrigin, CachedMouseWorldDirection);
// Assign the new mouse interaction interface
LastMouseInteractionInterface = MouseInteractionInterface;
// If the last mouse interaction interface is not none
if (LastMouseInteractionInterface != None)
{
// Call the mouse over function
LastMouseInteractionInterface.MouseOver(CachedMouseWorldOrigin, CachedMouseWorldDirection); // Call mouse over
}
}
}
else if (MouseInteractionInterface != None)
{
// Assign the new mouse interaction interface
LastMouseInteractionInterface = MouseInteractionInterface;
// Call the mouse over function
LastMouseInteractionInterface.MouseOver(CachedMouseWorldOrigin, CachedMouseWorldDirection);
}
if (LastMouseInteractionInterface != None)
{
// Handle left mouse button
if (PendingLeftPressed)
{
if (PendingLeftReleased)
{
// This is a left click, so discard
PendingLeftPressed = false;
PendingLeftReleased = false;
}
else
{
// Left is pressed
PendingLeftPressed = false;
LastMouseInteractionInterface.MouseLeftPressed(CachedMouseWorldOrigin, CachedMouseWorldDirection, HitLocation, HitNormal);
}
}
else if (PendingLeftReleased)
{
// Left is released
PendingLeftReleased = false;
LastMouseInteractionInterface.MouseLeftReleased(CachedMouseWorldOrigin, CachedMouseWorldDirection);
}
// Handle right mouse button
if (PendingRightPressed)
{
if (PendingRightReleased)
{
// This is a right click, so discard
PendingRightPressed = false;
PendingRightReleased = false;
}
else
{
// Right is pressed
PendingRightPressed = false;
LastMouseInteractionInterface.MouseRightPressed(CachedMouseWorldOrigin, CachedMouseWorldDirection, HitLocation, HitNormal);
}
}
else if (PendingRightReleased)
{
// Right is released
PendingRightReleased = false;
LastMouseInteractionInterface.MouseRightReleased(CachedMouseWorldOrigin, CachedMouseWorldDirection);
}
// Handle middle mouse button
if (PendingMiddlePressed)
{
if (PendingMiddleReleased)
{
// This is a middle click, so discard
PendingMiddlePressed = false;
PendingMiddleReleased = false;
}
else
{
// Middle is pressed
PendingMiddlePressed = false;
LastMouseInteractionInterface.MouseMiddlePressed(CachedMouseWorldOrigin, CachedMouseWorldDirection, HitLocation, HitNormal);
}
}
else if (PendingMiddleReleased)
{
PendingMiddleReleased = false;
LastMouseInteractionInterface.MouseMiddleReleased(CachedMouseWorldOrigin, CachedMouseWorldDirection);
}
// Handle middle mouse button scroll up
if (PendingScrollUp)
{
PendingScrollUp = false;
LastMouseInteractionInterface.MouseScrollUp(CachedMouseWorldOrigin, CachedMouseWorldDirection);
}
// Handle middle mouse button scroll down
if (PendingScrollDown)
{
PendingScrollDown = false;
LastMouseInteractionInterface.MouseScrollDown(CachedMouseWorldOrigin, CachedMouseWorldDirection);
}
}
}
function MouseInterfaceInteractionInterface GetMouseActor(optional out Vector HitLocation, optional out Vector HitNormal)
{
local MouseInterfaceInteractionInterface MouseInteractionInterface;
local MouseInterfacePlayerInput MouseInterfacePlayerInput;
local Vector2D MousePosition;
local Actor HitActor;
// Ensure that we have a valid canvas and player owner
if (Canvas == None || PlayerOwner == None)
{
return None;
}
// Type cast to get the new player input
MouseInterfacePlayerInput = MouseInterfacePlayerInput(PlayerOwner.PlayerInput);
// Ensure that the player input is valid
if (MouseInterfacePlayerInput == None)
{
return None;
}
// We stored the mouse position as an IntPoint, but it's needed as a Vector2D
MousePosition.X = MouseInterfacePlayerInput.MousePosition.X;
MousePosition.Y = MouseInterfacePlayerInput.MousePosition.Y;
// Deproject the mouse position and store it in the cached vectors
Canvas.DeProject(MousePosition, CachedMouseWorldOrigin, CachedMouseWorldDirection);
// Perform a trace actor interator. An interator is used so that we get the top most mouse interaction
// interface. This covers cases when other traceable objects (such as static meshes) are above mouse
// interaction interfaces.
ForEach TraceActors(class'Actor', HitActor, HitLocation, HitNormal, CachedMouseWorldOrigin + CachedMouseWorldDirection * 65536.f, CachedMouseWorldOrigin,,, TRACEFLAG_Bullet)
{
// Type cast to see if the HitActor implements that mouse interaction interface
MouseInteractionInterface = MouseInterfaceInteractionInterface(HitActor);
if (MouseInteractionInterface != None)
{
return MouseInteractionInterface;
}
}
return None;
}
function Vector GetMouseWorldLocation()
{
local MouseInterfacePlayerInput MouseInterfacePlayerInput;
local Vector2D MousePosition;
local Vector MouseWorldOrigin, MouseWorldDirection, HitLocation, HitNormal;
// Ensure that we have a valid canvas and player owner
if (Canvas == None || PlayerOwner == None)
{
return Vect(0, 0, 0);
}
// Type cast to get the new player input
MouseInterfacePlayerInput = MouseInterfacePlayerInput(PlayerOwner.PlayerInput);
// Ensure that the player input is valid
if (MouseInterfacePlayerInput == None)
{
return Vect(0, 0, 0);
}
// We stored the mouse position as an IntPoint, but it's needed as a Vector2D
MousePosition.X = MouseInterfacePlayerInput.MousePosition.X;
MousePosition.Y = MouseInterfacePlayerInput.MousePosition.Y;
// Deproject the mouse position and store it in the cached vectors
Canvas.DeProject(MousePosition, MouseWorldOrigin, MouseWorldDirection);
// Perform a trace to get the actual mouse world location.
Trace(HitLocation, HitNormal, MouseWorldOrigin + MouseWorldDirection * 65536.f, MouseWorldOrigin , true,,, TRACEFLAG_Bullet);
return HitLocation;
}
defaultproperties
{
// Set to false if you wish to use Unreal's player input to retrieve the mouse coordinates
UsingScaleForm=true
CursorColor=(R=255,G=255,B=255,A=255)
CursorTexture=Texture2D'EngineResources.Cursors.Arrow'
}
- For every frame that is rendered, we render the mouse cursor
- Get the current mouse interaction interface by performing a trace within the world. If the current mouse interaction interface differs from the last one, call the mouse over and or mouse out functions appropriately.
- If we have a valid mouse interaction interface, the HUD then handles the deferred mouse input
- For each mouse input call the appropriate interface function and reset the boolean
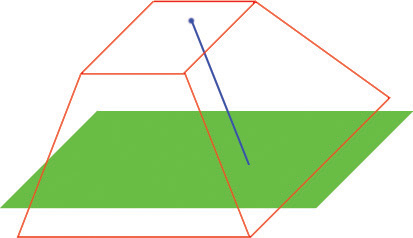
I just want to get the mouse 3D coordinates!
To get the mouse 3D coordinates based on the mouse 2D coordinates, you can use this function within your HUD class. The HUD class is required because the Deproject function is required.
function Vector GetMouseWorldLocation()
{
local MouseInterfacePlayerInput MouseInterfacePlayerInput;
local Vector2D MousePosition;
local Vector MouseWorldOrigin, MouseWorldDirection, HitLocation, HitNormal;
// Ensure that we have a valid canvas and player owner
if (Canvas == None || PlayerOwner == None)
{
return Vect(0, 0, 0);
}
// Type cast to get the new player input
MouseInterfacePlayerInput = MouseInterfacePlayerInput(PlayerOwner.PlayerInput);
// Ensure that the player input is valid
if (MouseInterfacePlayerInput == None)
{
return Vect(0, 0, 0);
}
// We stored the mouse position as an IntPoint, but it's needed as a Vector2D
MousePosition.X = MouseInterfacePlayerInput.MousePosition.X;
MousePosition.Y = MouseInterfacePlayerInput.MousePosition.Y;
// Deproject the mouse position and store it in the cached vectors
Canvas.DeProject(MousePosition, MouseWorldOrigin, MouseWorldDirection);
// Perform a trace to get the actual mouse world location.
Trace(HitLocation, HitNormal, MouseWorldOrigin + MouseWorldDirection * 65536.f, MouseWorldOrigin , true,,, TRACEFLAG_Bullet);
return HitLocation;
}
Related topics
Adding the Kismet Mouse Input Event
class SeqEvent_MouseInput extends SequenceEvent;
var Vector HitLocation;
var Vector HitNormal;
var Vector MouseWorldOrigin;
var Vector MouseWorldDirection;
event Activated()
{
local MouseInterfaceInteractionInterface MouseInteractionInterface;
// Type cast the originator to ensure that it is a mouse interaction interface
MouseInteractionInterface = MouseInterfaceInteractionInterface(Originator);
if (MouseInteractionInterface != None)
{
// Get the appropriate values so we can push them out when the event is activated
MouseWorldOrigin = MouseInteractionInterface.GetMouseWorldOrigin();
MouseWorldDirection = MouseInteractionInterface.GetMouseWorldDirection();
HitLocation = MouseInteractionInterface.GetHitLocation();
HitNormal = MouseInteractionInterface.GetHitNormal();
}
}
defaultproperties
{
ObjName="Mouse Input"
ObjCategory="Input"
bPlayerOnly=false
MaxTriggerCount=0
OutputLinks(0)=(LinkDesc="Left Pressed")
OutputLinks(1)=(LinkDesc="Left Released")
OutputLinks(2)=(LinkDesc="Right Pressed")
OutputLinks(3)=(LinkDesc="Right Released")
OutputLinks(4)=(LinkDesc="Middle Pressed")
OutputLinks(5)=(LinkDesc="Middle Released")
OutputLinks(6)=(LinkDesc="Scroll Up")
OutputLinks(7)=(LinkDesc="Scroll Down")
OutputLinks(8)=(LinkDesc="Mouse Over")
OutputLinks(9)=(LinkDesc="Mouse Out")
VariableLinks(1)=(ExpectedType=class'SeqVar_Vector',LinkDesc="HitLocation",bWriteable=true,PropertyName=HitLocation)
VariableLinks(2)=(ExpectedType=class'SeqVar_Vector',LinkDesc="HitNormal",bWriteable=true,PropertyName=HitNormal)
VariableLinks(3)=(ExpectedType=class'SeqVar_Vector',LinkDesc="MouseWorldOrigin",bWriteable=true,PropertyName=MouseWorldOrigin)
VariableLinks(4)=(ExpectedType=class'SeqVar_Vector',LinkDesc="MouseWorldDirection",bWriteable=true,PropertyName=MouseWorldDirection)
}
Related topics
Adding a subclassed KActor as an example
class MouseInterfaceKActor extends KActor
Implements(MouseInterfaceInteractionInterface);
var Vector CachedMouseHitLocation;
var Vector CachedMouseHitNormal;
var Vector CachedMouseWorldOrigin;
var Vector CachedMouseWorldDirection;
// ===
// MouseInterfaceInteractionInterface implementation
// ===
function MouseLeftPressed(Vector MouseWorldOrigin, Vector MouseWorldDirection, Vector HitLocation, Vector HitNormal)
{
CachedMouseWorldOrigin = MouseWorldOrigin;
CachedMouseWorldDirection = MouseWorldDirection;
CachedMouseHitLocation = HitLocation;
CachedMouseHitNormal = HitNormal;
TriggerEventClass(class'SeqEvent_MouseInput', Self, 0);
}
function MouseLeftReleased(Vector MouseWorldOrigin, Vector MouseWorldDirection)
{
CachedMouseWorldOrigin = MouseWorldOrigin;
CachedMouseWorldDirection = MouseWorldDirection;
CachedMouseHitLocation = Vect(0.f, 0.f, 0.f);
CachedMouseHitNormal = Vect(0.f, 0.f, 0.f);
TriggerEventClass(class'SeqEvent_MouseInput', Self, 1);
}
function MouseRightPressed(Vector MouseWorldOrigin, Vector MouseWorldDirection, Vector HitLocation, Vector HitNormal)
{
CachedMouseWorldOrigin = MouseWorldOrigin;
CachedMouseWorldDirection = MouseWorldDirection;
CachedMouseHitLocation = HitLocation;
CachedMouseHitNormal = HitNormal;
TriggerEventClass(class'SeqEvent_MouseInput', Self, 2);
}
function MouseRightReleased(Vector MouseWorldOrigin, Vector MouseWorldDirection)
{
CachedMouseWorldOrigin = MouseWorldOrigin;
CachedMouseWorldDirection = MouseWorldDirection;
CachedMouseHitLocation = Vect(0.f, 0.f, 0.f);
CachedMouseHitNormal = Vect(0.f, 0.f, 0.f);
TriggerEventClass(class'SeqEvent_MouseInput', Self, 3);
}
function MouseMiddlePressed(Vector MouseWorldOrigin, Vector MouseWorldDirection, Vector HitLocation, Vector HitNormal)
{
CachedMouseWorldOrigin = MouseWorldOrigin;
CachedMouseWorldDirection = MouseWorldDirection;
CachedMouseHitLocation = HitLocation;
CachedMouseHitNormal = HitNormal;
TriggerEventClass(class'SeqEvent_MouseInput', Self, 4);
}
function MouseMiddleReleased(Vector MouseWorldOrigin, Vector MouseWorldDirection)
{
CachedMouseWorldOrigin = MouseWorldOrigin;
CachedMouseWorldDirection = MouseWorldDirection;
CachedMouseHitLocation = Vect(0.f, 0.f, 0.f);
CachedMouseHitNormal = Vect(0.f, 0.f, 0.f);
TriggerEventClass(class'SeqEvent_MouseInput', Self, 5);
}
function MouseScrollUp(Vector MouseWorldOrigin, Vector MouseWorldDirection)
{
CachedMouseWorldOrigin = MouseWorldOrigin;
CachedMouseWorldDirection = MouseWorldDirection;
CachedMouseHitLocation = Vect(0.f, 0.f, 0.f);
CachedMouseHitNormal = Vect(0.f, 0.f, 0.f);
TriggerEventClass(class'SeqEvent_MouseInput', Self, 6);
}
function MouseScrollDown(Vector MouseWorldOrigin, Vector MouseWorldDirection)
{
CachedMouseWorldOrigin = MouseWorldOrigin;
CachedMouseWorldDirection = MouseWorldDirection;
CachedMouseHitLocation = Vect(0.f, 0.f, 0.f);
CachedMouseHitNormal = Vect(0.f, 0.f, 0.f);
TriggerEventClass(class'SeqEvent_MouseInput', Self, 7);
}
function MouseOver(Vector MouseWorldOrigin, Vector MouseWorldDirection)
{
CachedMouseWorldOrigin = MouseWorldOrigin;
CachedMouseWorldDirection = MouseWorldDirection;
CachedMouseHitLocation = Vect(0.f, 0.f, 0.f);
CachedMouseHitNormal = Vect(0.f, 0.f, 0.f);
TriggerEventClass(class'SeqEvent_MouseInput', Self, 8);
}
function MouseOut(Vector MouseWorldOrigin, Vector MouseWorldDirection)
{
CachedMouseWorldOrigin = MouseWorldOrigin;
CachedMouseWorldDirection = MouseWorldDirection;
CachedMouseHitLocation = Vect(0.f, 0.f, 0.f);
CachedMouseHitNormal = Vect(0.f, 0.f, 0.f);
TriggerEventClass(class'SeqEvent_MouseInput', Self, 9);
}
function Vector GetHitLocation()
{
return CachedMouseHitLocation;
}
function Vector GetHitNormal()
{
return CachedMouseHitNormal;
}
function Vector GetMouseWorldOrigin()
{
return CachedMouseWorldOrigin;
}
function Vector GetMouseWorldDirection()
{
return CachedMouseWorldDirection;
}
defaultproperties
{
SupportedEvents(4)=class'SeqEvent_MouseInput'
}
- When any of the interface implementation functions are executed via the HUD, we trigger the attached Mouse Input Kismet node. The number at end of the trigger call is the output index.
Using the Kismet Mouse Input Event
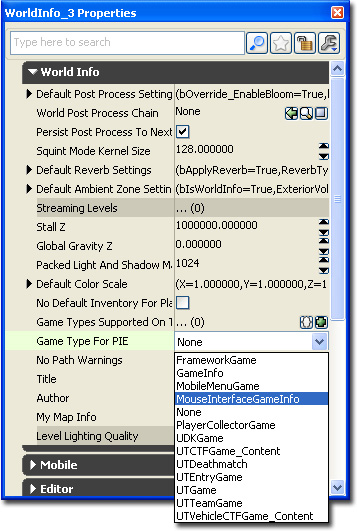 Expand the "Lightmass" tab and uncheck the "Use Global Illumination" check box. There is no need to use light mass for the test map.
Expand the "Lightmass" tab and uncheck the "Use Global Illumination" check box. There is no need to use light mass for the test map.
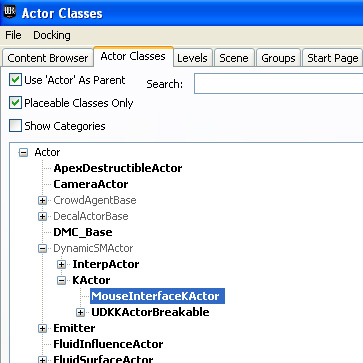
 Open up the "Content Browser" and select the "Actor Classes" tab. From there expand the class tree select the "MouseInterfaceKActor". This is so that when you open up the context menu within the world viewport, it will allow you to add it within the world.
Open up the "Content Browser" and select the "Actor Classes" tab. From there expand the class tree select the "MouseInterfaceKActor". This is so that when you open up the context menu within the world viewport, it will allow you to add it within the world.
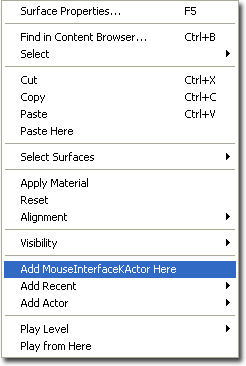
 Right click within the world viewport to open the viewport context menu. Select and click "Add MouseInterfaceKActor Here" to add a MouseInterfaceKActor.
Right click within the world viewport to open the viewport context menu. Select and click "Add MouseInterfaceKActor Here" to add a MouseInterfaceKActor.
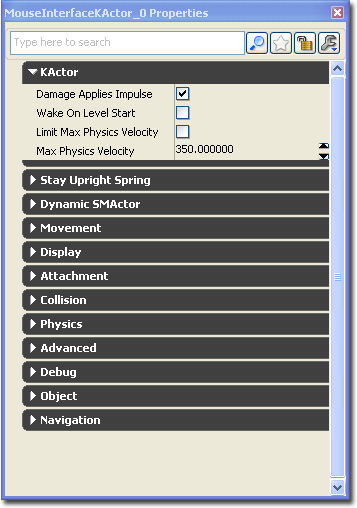
 Because the MouseInterfaceKActor doesn't have a visible static mesh, it will first appear as the selected transform widget (selection, movement, rotation or scaling widget). Press F4 to open up the actors property window. Click on the padlock icon at the top to set the selection.
Because the MouseInterfaceKActor doesn't have a visible static mesh, it will first appear as the selected transform widget (selection, movement, rotation or scaling widget). Press F4 to open up the actors property window. Click on the padlock icon at the top to set the selection.
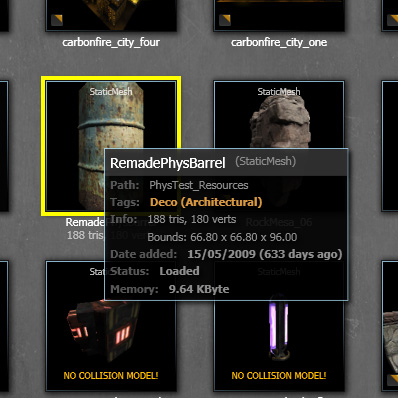
 Find an interesting static mesh within the "Content Browser". Select it within the "Content Browser".
Find an interesting static mesh within the "Content Browser". Select it within the "Content Browser".
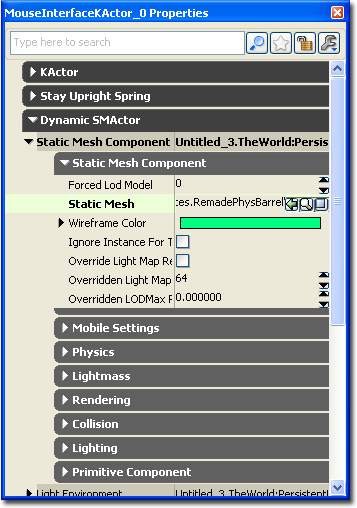
 Expand the "Dynamic SMActor" tab, expand the "Static Mesh Component" object, then lastly the "Static Mesh Component" tab. Press the green arrow next to the "Static Mesh" field. This will set the static mesh you've selected in the "Content Browser". You should see the barrel appear within the world viewport.
Expand the "Dynamic SMActor" tab, expand the "Static Mesh Component" object, then lastly the "Static Mesh Component" tab. Press the green arrow next to the "Static Mesh" field. This will set the static mesh you've selected in the "Content Browser". You should see the barrel appear within the world viewport.
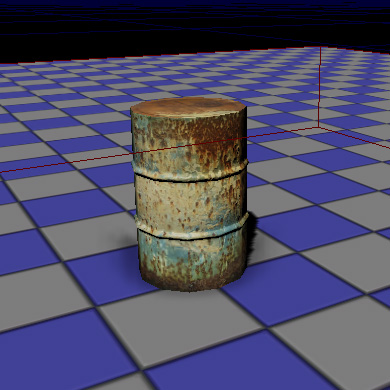
 Add the necessary lighting within the level and compile the level.
Add the necessary lighting within the level and compile the level.
 Open up the Kismet window by pressing
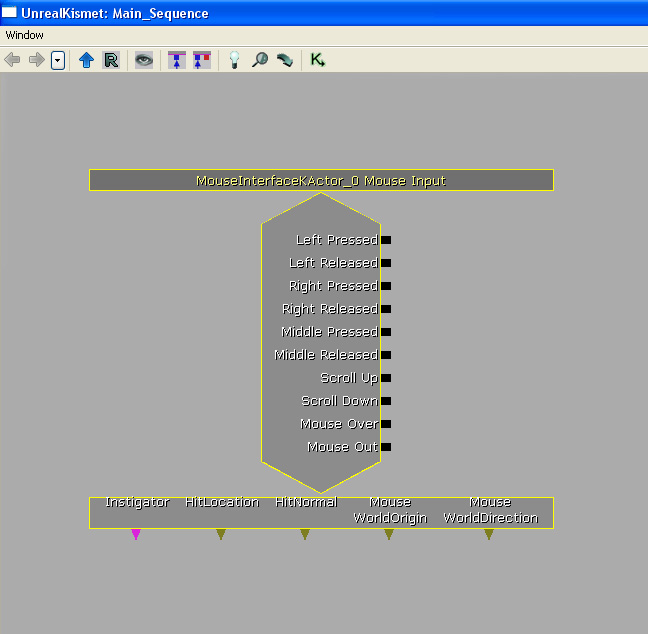
Open up the Kismet window by pressing  This is our Mouse Input event. As you can see, all of the output links refer to the mouse input types that may occur. The event also outputs various variables that we can also use.
This is our Mouse Input event. As you can see, all of the output links refer to the mouse input types that may occur. The event also outputs various variables that we can also use.
 To test our Mouse Input event, let's create a few log actions.
To test our Mouse Input event, let's create a few log actions.
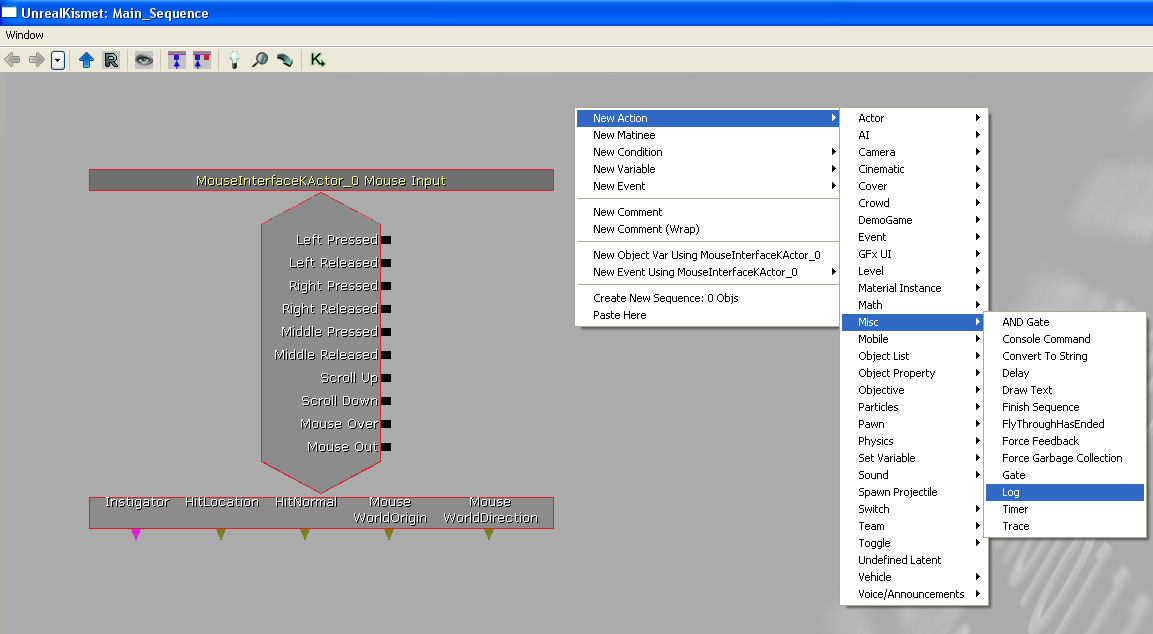 Set the log action to output some text that is appropriate for the event output we want to test.
Set the log action to output some text that is appropriate for the event output we want to test.
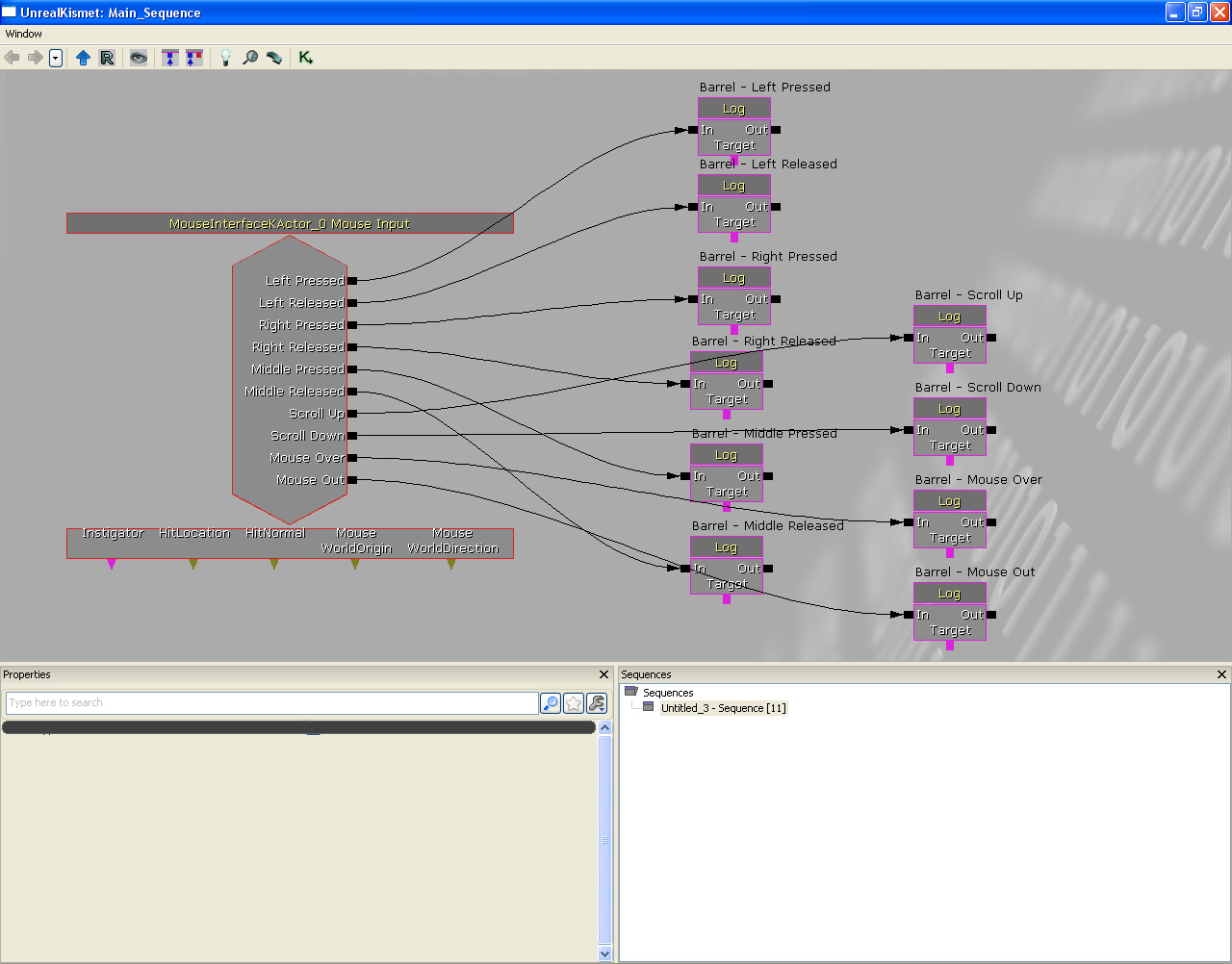
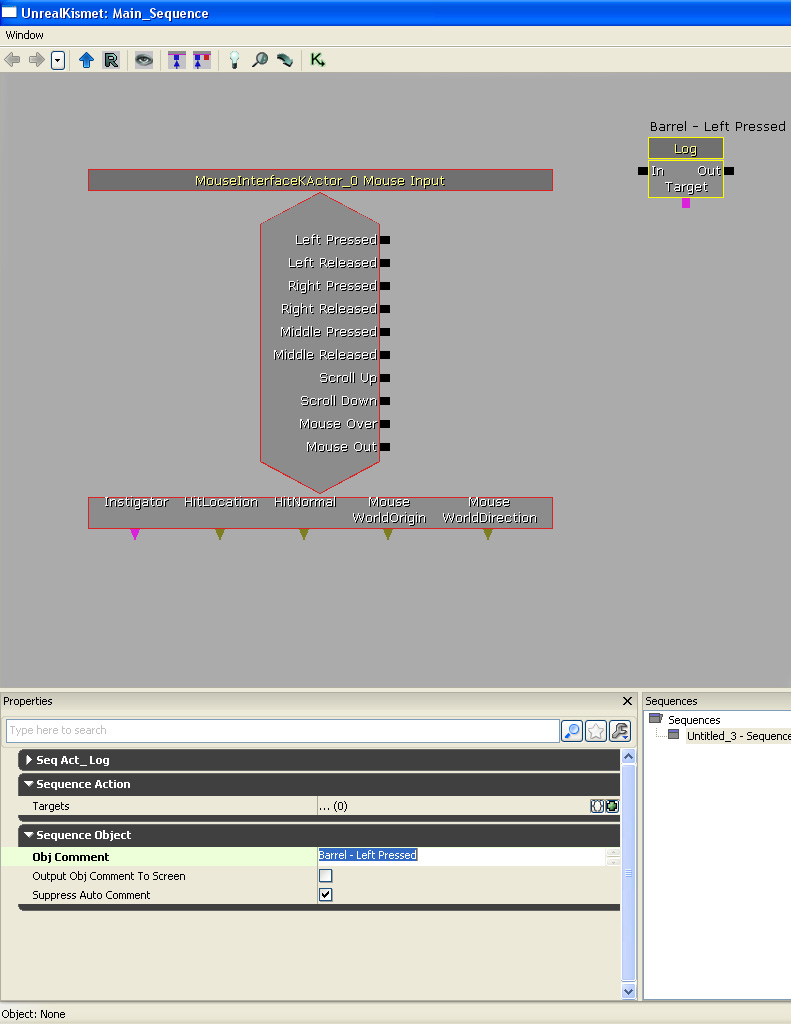 Create more log actions to test all of the event outputs. Connect them all up appropriately.
Create more log actions to test all of the event outputs. Connect them all up appropriately.
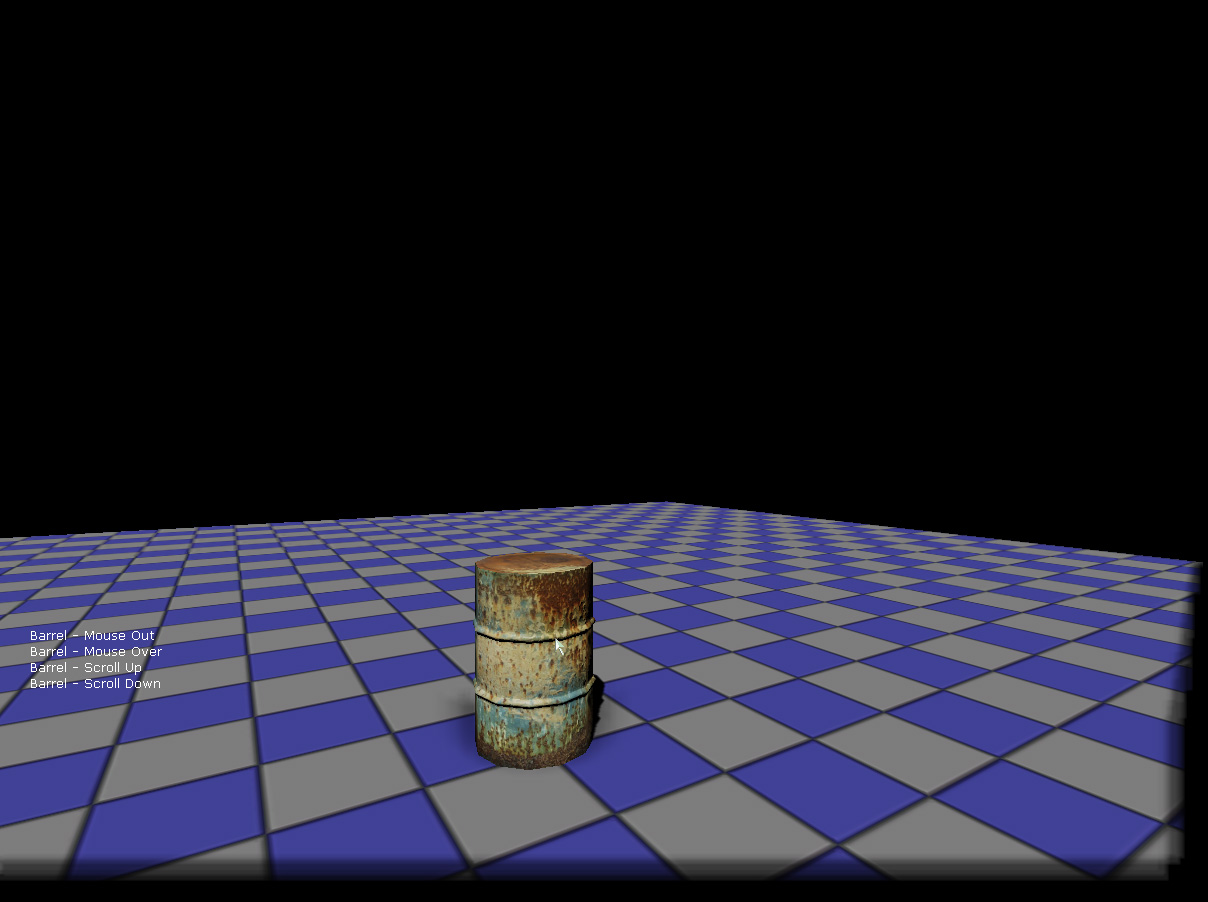
 Run the level within PIE and you should be able to test the mouse input Kismet interface. Remember that the mouse buttons and scrolling are only responsive when the mouse is over the MouseInterfaceKActor.
Run the level within PIE and you should be able to test the mouse input Kismet interface. Remember that the mouse buttons and scrolling are only responsive when the mouse is over the MouseInterfaceKActor.
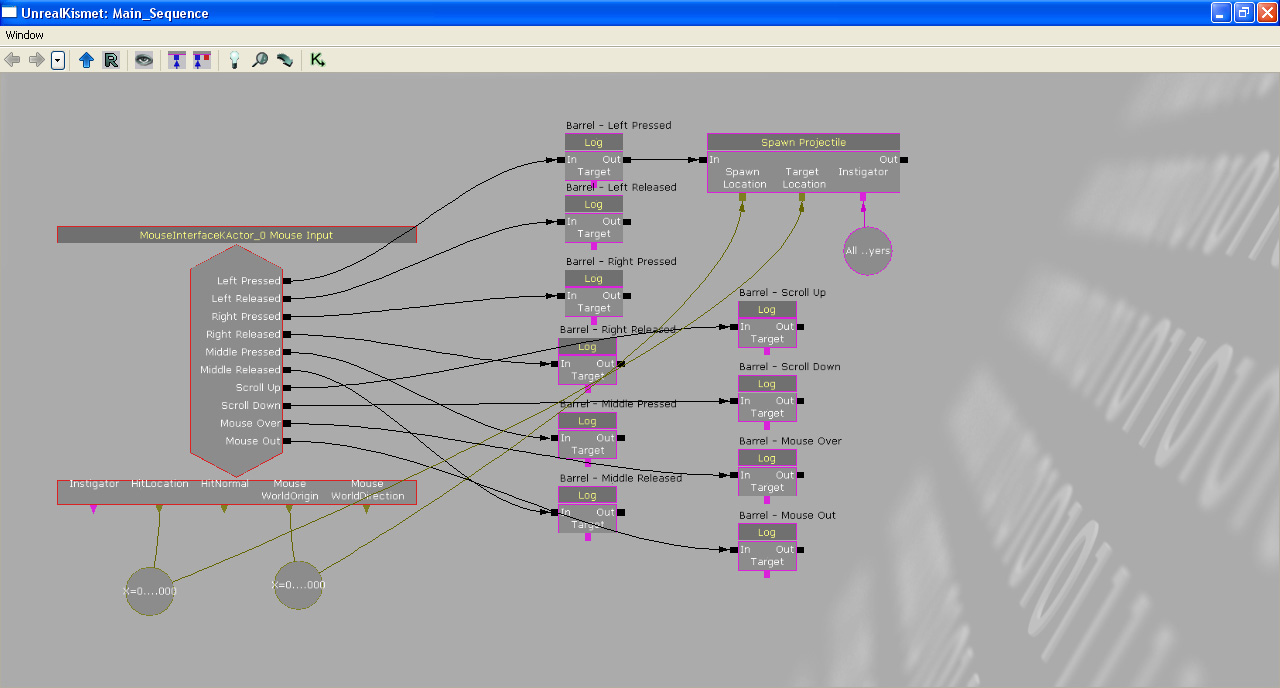
 Let's expand this example by creating a sequence which allows us to shoot at the MouseInterfaceKActor. Start by creating a new vector variable. This is so that we can store the mouse origin and the mouse hit location.
Let's expand this example by creating a sequence which allows us to shoot at the MouseInterfaceKActor. Start by creating a new vector variable. This is so that we can store the mouse origin and the mouse hit location.
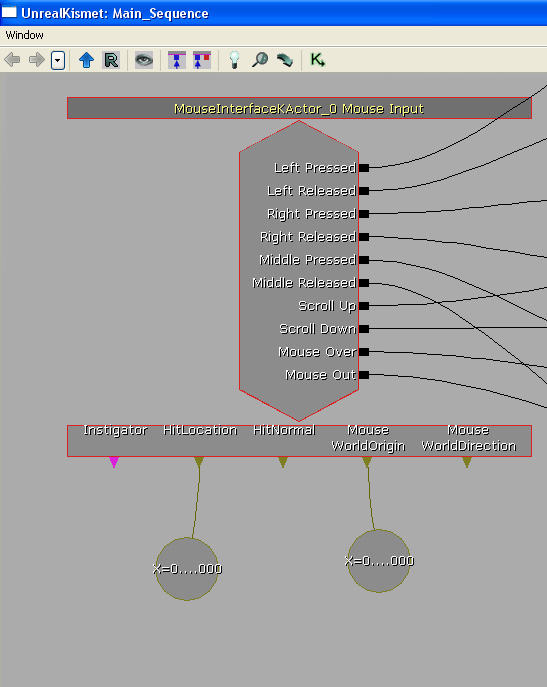
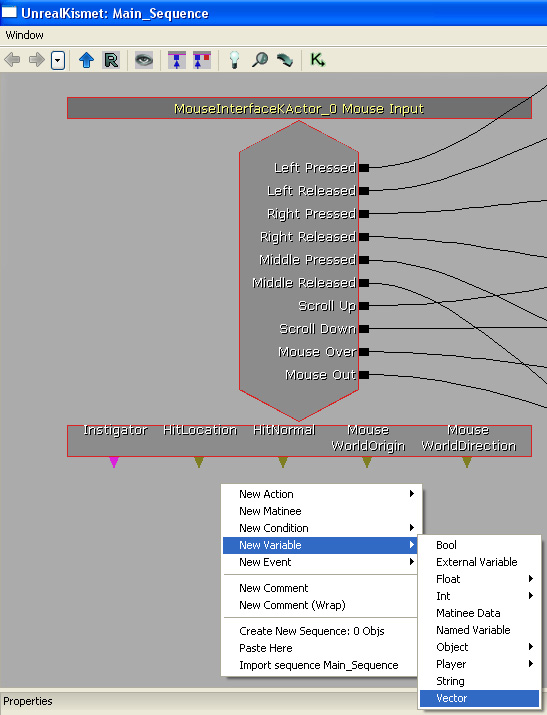 Bind the vector variables to the event's variable outputs, "HitLocation" and "Mouse WorldOrigin".
Bind the vector variables to the event's variable outputs, "HitLocation" and "Mouse WorldOrigin".
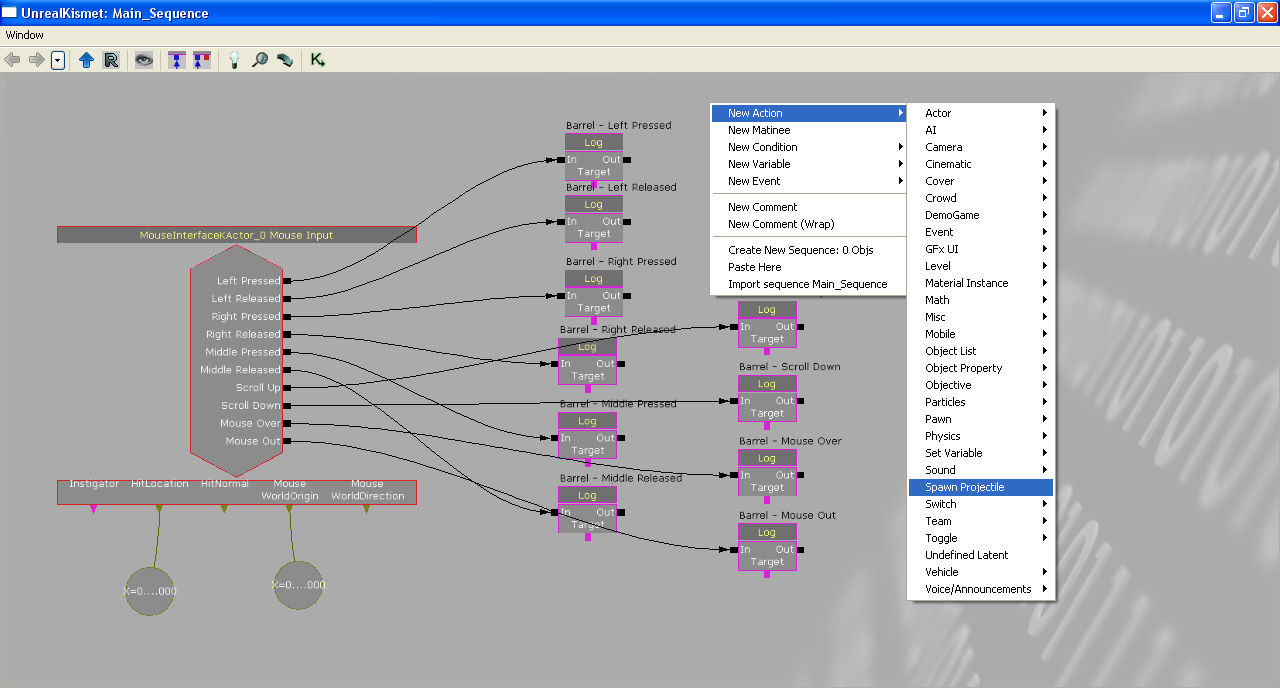
 Add a new "Spawn Projectile" action. This creates a projectile when the action is executed.
Add a new "Spawn Projectile" action. This creates a projectile when the action is executed.
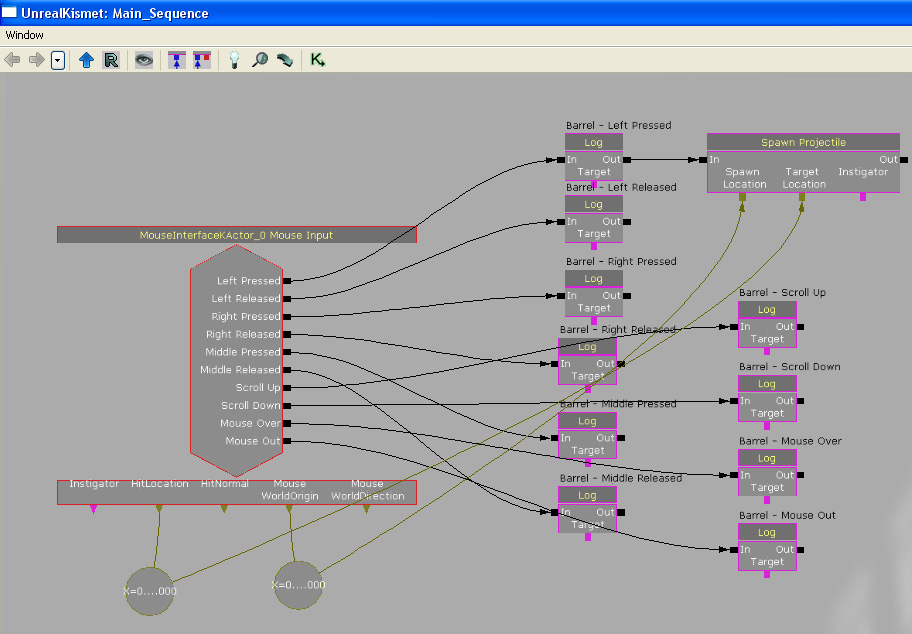
 This is the newly created "Spawn Projectile" action.
This is the newly created "Spawn Projectile" action.
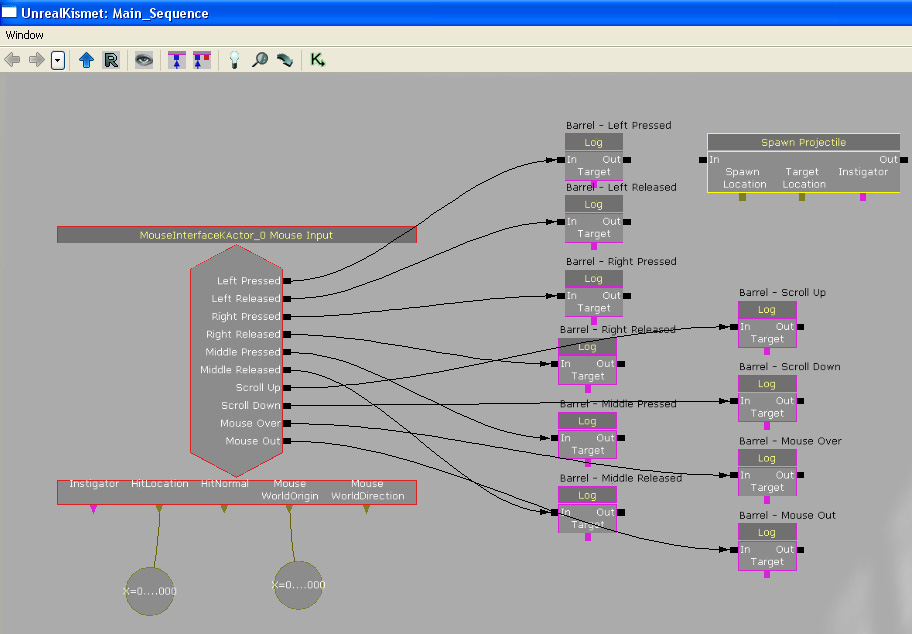 Connect the "Spawn Projectile" action to the "Log" action which is activated when the left mouse button is pressed. Connect the "Mouse WorldOrigin" variable to the "Spawn Location" input on the "Spawn Projectile" event. Connect the "HitLocation" variable to the "Target Location" input on the "Spawn Projectile" event. This will cause the "Spawn Projectile" to spawn a projectile at the mouse world origin location that will travel towards the mouse hit location. Thus making it look like that we are shooting at the MouseInterfaceKActor in the world.
Connect the "Spawn Projectile" action to the "Log" action which is activated when the left mouse button is pressed. Connect the "Mouse WorldOrigin" variable to the "Spawn Location" input on the "Spawn Projectile" event. Connect the "HitLocation" variable to the "Target Location" input on the "Spawn Projectile" event. This will cause the "Spawn Projectile" to spawn a projectile at the mouse world origin location that will travel towards the mouse hit location. Thus making it look like that we are shooting at the MouseInterfaceKActor in the world.
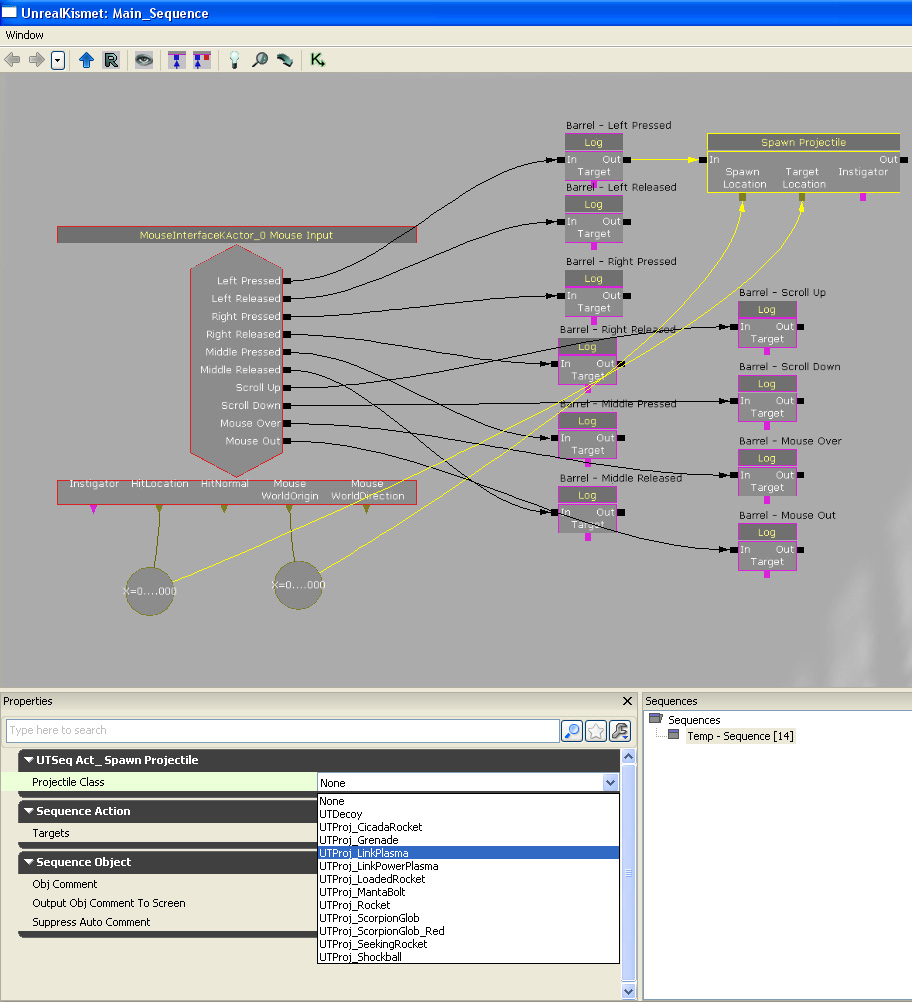
 Set what kind of projectile to spawn.
Set what kind of projectile to spawn.
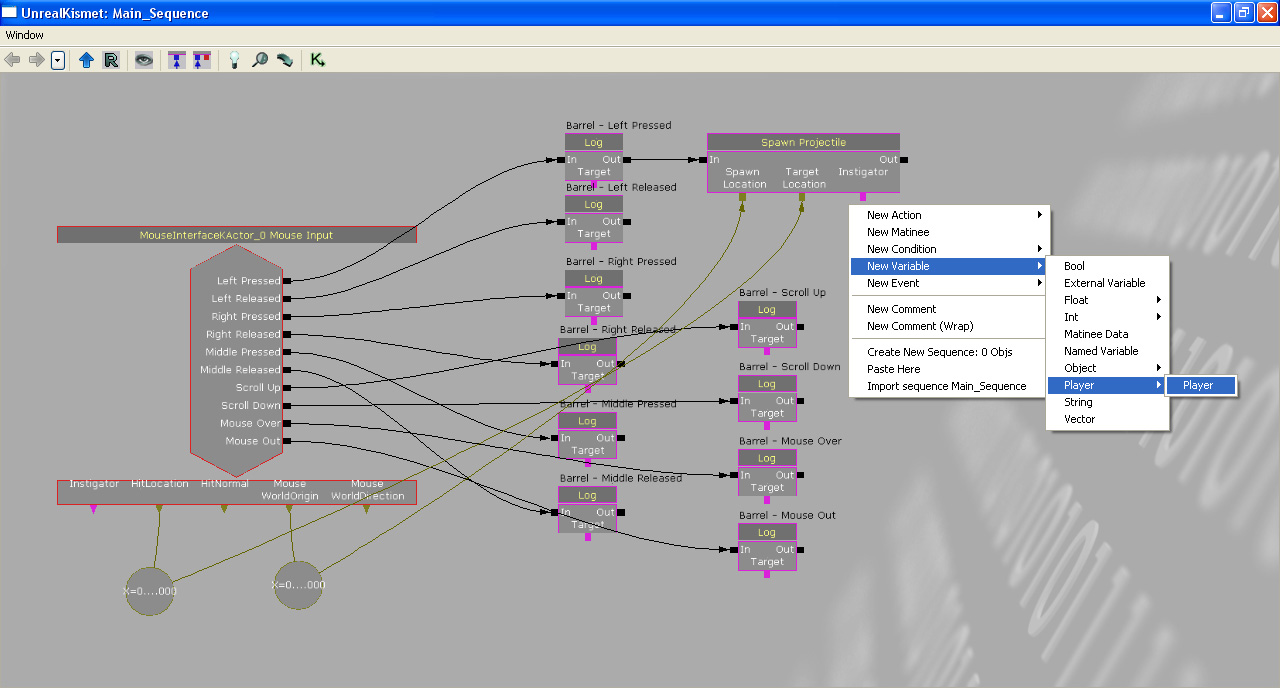
 Add an "All Players" variable. This is a required input of the "Spawn Projectile" action.
Add an "All Players" variable. This is a required input of the "Spawn Projectile" action.
 Here is the newly created "All Players" variable.
Here is the newly created "All Players" variable.
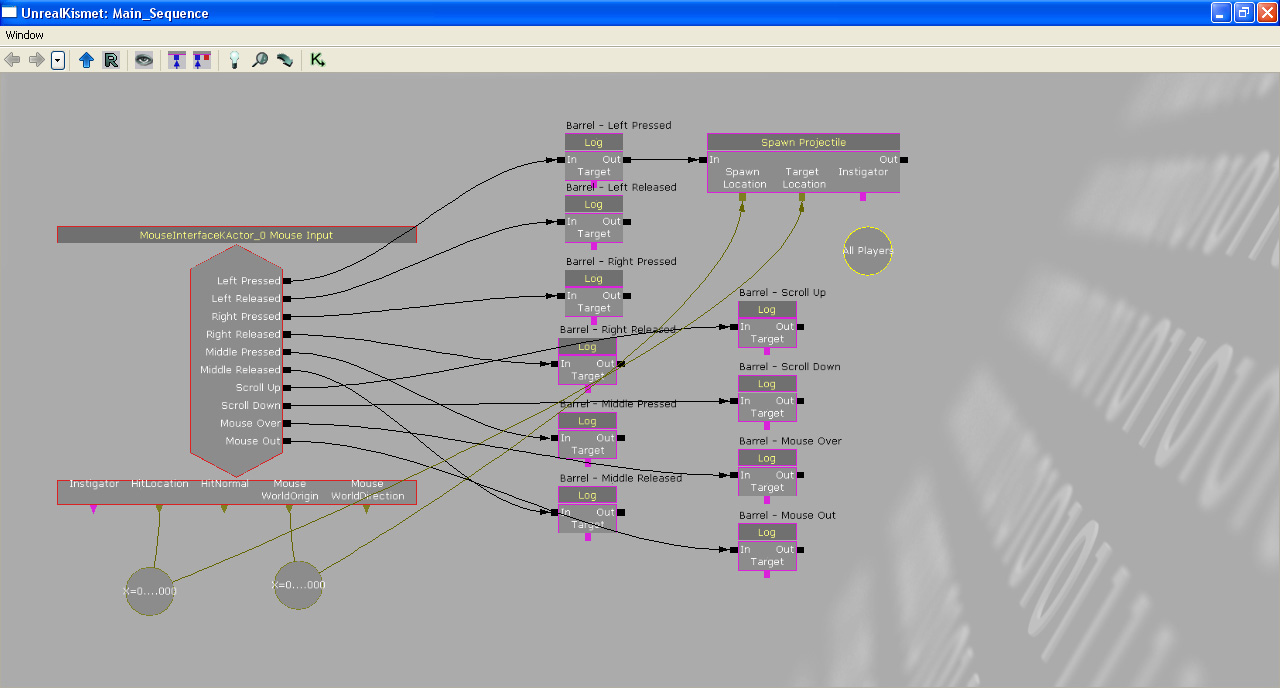 Connect the "All Players" variable to the "Spawn Projectile".
Connect the "All Players" variable to the "Spawn Projectile".
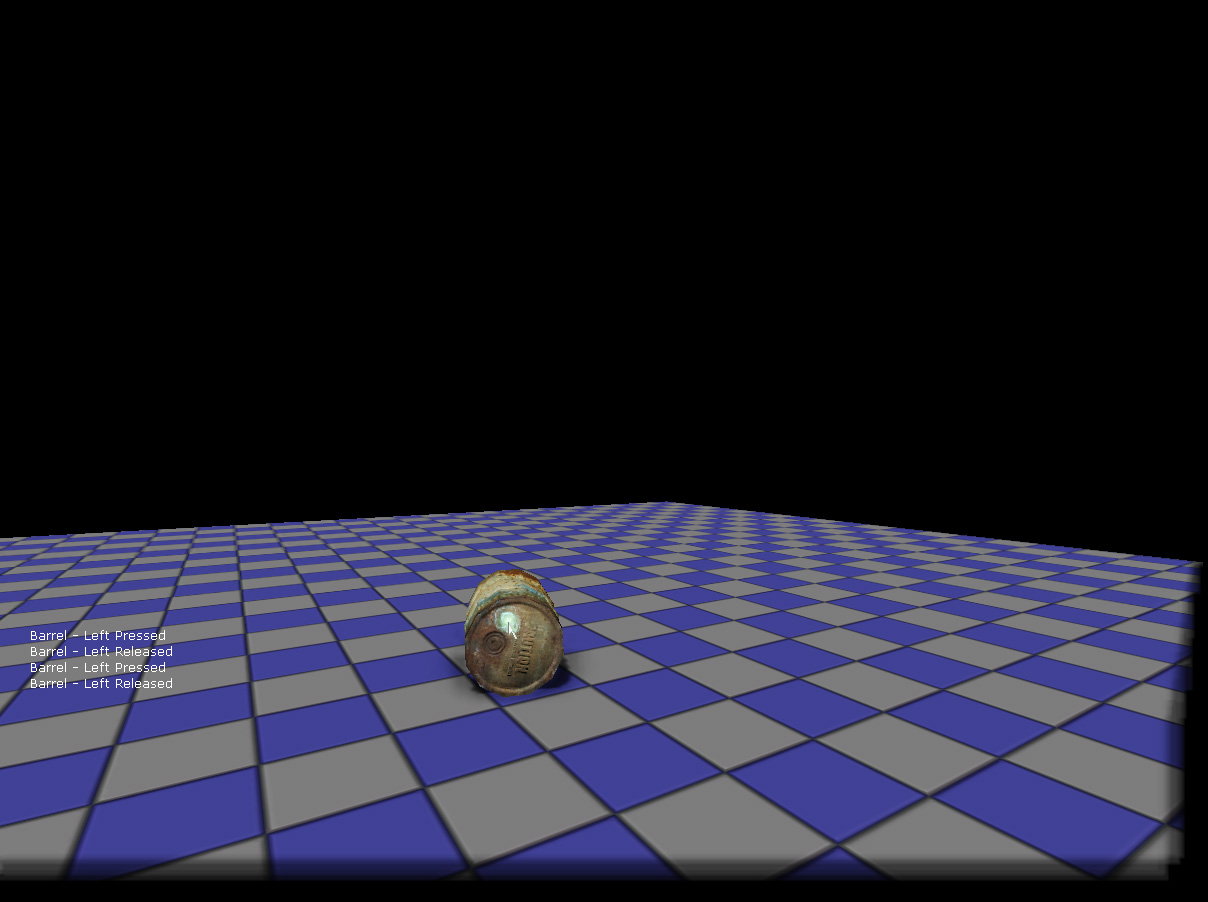
 Run PIE and test the Kismet. You should now be able to fire at the MouseInterfaceKActor.
Run PIE and test the Kismet. You should now be able to fire at the MouseInterfaceKActor.
Related topics
Downloads
- Download the content used in this gem. (MouseInterface.zip)
